 data-pin-media=”https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/qZdXC5h9Dv3AohH58aHTp5.jpg” data-pin-nopin=”true” fetchpriority=”high”>
data-pin-media=”https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/qZdXC5h9Dv3AohH58aHTp5.jpg” data-pin-nopin=”true” fetchpriority=”high”>
(Image credit: WH Pics by means of Shutterstock)
The capability to make art has actually typically been thought about a trademark of our types. Over a century earlier, prehistorians even had difficulty thinking that contemporary people from the Upper Paleolithic(in between 45,000 and 12,000 years ago)can creative style.
Discoveries of uncontrovertibly old art work from the caverns and rockshelters of Europe quickly eliminated their doubts. What of the Neanderthals; an ancient, large-brained sis group to our own types? We now understand that they can making art too.
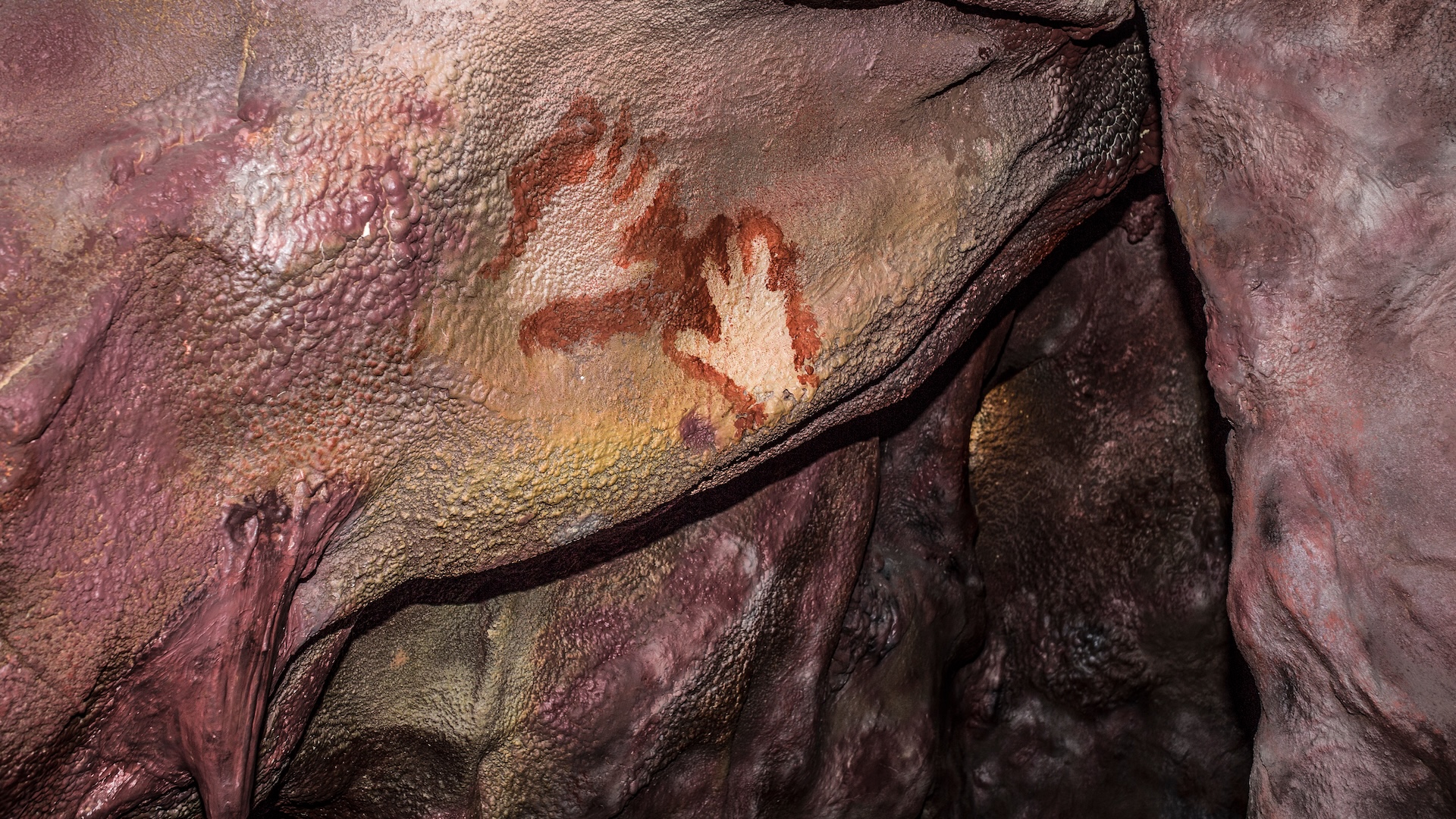
At present, all of the Neanderthal proof is non-figurative– they have no representations of animals, consisting of people. This latter type of art was possibly special to HumankindRather, the Neanderthal examples include hand stencils, made by blowing pigment over the hand, finger flutings– where the fingers were pushed into a soft surface area– and geometric markings.Neanderthals lived in western Eurasia from about 400,000 years ago up until their termination about 40,000 years earlier and have actually typically been caricatured as the stereotypical “cavemen”
Concerns about their cognitive and behavioral elegance have actually never ever rather disappeared, and whether they produced art is at the leading edge of this concern.
In spite of the reality that we understand that Neanderthals can producing precious jewelry and utilizing colored pigments, there has actually been much objection to the concept that they checked out deep caverns and left art on the walls.
Current work has actually verified beyond doubt that they did. In 3 Spanish caverns — La Pasiega in Cantabria, Maltravieso in Extremadura and Ardales in Malaga, Neanderthals produced direct indications, geometric shapes, hand stencils, and handprints utilizing pigments. In La Roche Cotarda collapse the Loire Valley, France, Neanderthals left a range of lines and shapes in finger flutings (the lines that fingers leave on a soft surface area).
Get the world’s most interesting discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
And deep in the Bruniquel cavernsouthwest France, they broke off stalactites into areas of comparable length and built a big oval wall of them, setting fires on top of it. This was not a shelter however something odder, and if it was built in a contemporary art gallery we had actually no doubt presume it was setup art.
Now that we have reputable examples of Neanderthal art on cavern walls in France and Spain, more discoveries are inescapable. The task is hard due to the fact that of troubles in developing the age of Paleolithic cavern art. It is typically the focus of extreme dispute amongst professionals.
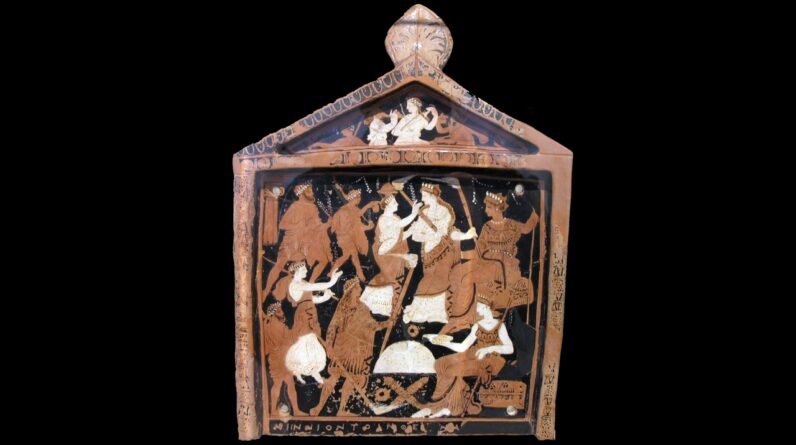
Art made by Neanderthals on
a cavern wall at La Roche Cotard in France.
( Image credit: Courtesy Jean-Claude Marquet, Paul Pettitt )Relative dating plans based upon the design and styles of cavern art and contrasts of things recuperated from outdated historical levels have actually shown helpful, however they have their limitations.
To produce genuine ages needs a minimum of among 3 conditions. The very first is the existence of a charcoal pigment which can be dated utilizing the radiocarbon technique. This will develop precisely when the charcoal was produced (when its wood passed away). Black pigments are typically from minerals (manganese) and for that reason a big quantity of black colored cavern art is just not dateable.
A more issue is that the production of the charcoal might or might not be of the exact same age as the date that it was utilized as a pigment. I might get some 30,000-year-old charcoal from a cavern flooring and compose “Paul was here” on a cavern wall. The radiocarbon date would not show when my grafitto was in fact made.
A 2nd condition is the existence of calcite flowstones (stalactites and stalagmites) that have actually formed over the art. If they demonstrably grew on top of an art piece, then they should be more youthful than it. A dating approach based upon the decay of uranium into an isotope– a specific type– of the aspect thorium can be utilized to develop precisely when flowstones formed, producing a minimum age for the art below.
I became part of a group who utilized this technique to date flowstones overlying red pigment art in the 3 Spanish caverns pointed out previously, showing that hand stencils, dots and color washes should have been produced over 64,000 years agoThis is a minimum age: the real age of the images might be much older.
Even at its youngest variety, the images precede the earliest arrival of contemporary people (Humankindin Iberia by a minimum of 22,000 years. As Middle Paleolithic archaeology– the calling cards of the Neanderthals– prevails in all 3 caverns, the easiest analysis that fits the dating is that the authors of the images were Neanderthals.
Objections to our outcomes overlooked supporting info we had actually released. Did the outdated samples truly overlie the art? They did. Can we rely on the method? We have for half a century.
The 3rd condition has actually simply offered more proof of Neanderthal creative activity. Meandering lines left by tracing fingers along the soft muds of the walls of the Roche Cotard cave expose another kind of engaging with this strange below ground world. These markings consist of wavy, parallel and curved lines in arranged plans that reveal they were made intentionally.
The dating of sediments which formed over its entryway program that it was entirely sealed no behind 54,000 years back– most likely previously. Just like our Spanish examples, this was long previously Humankind shown up in the area and the cavern includes just tools made by Neanderthals. It includes another art kind to the Neanderthal collection.
Even ardent sceptics need to concur that this information unambiguously expose creative activities in deep caverns which can just have actually been made by Neanderthals.
The art might represent Neanderthal people ending up being more knowledgeable about their own firm on the planet. It may make up the very first proof of engagement with a fictional world. The coming years will no doubt expose much more topics for argument.
This edited short article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Check out the initial post
Paul Pettitt is a teacher of Archaeology at Durham University who concentrates on the European Middle and Upper Paleolithic, concentrating on Neanderthal habits, Paleolithic art, and early human mortuary activity. He co-discovered Britain’s only examples of Paleolithic cavern art at Creswell Crags and has actually performed excavations there and at Kent’s Cavern. His research study integrates archaeology, chronometry, and psychology to check out the development of symbolic and routine habits in early human beings.
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.







