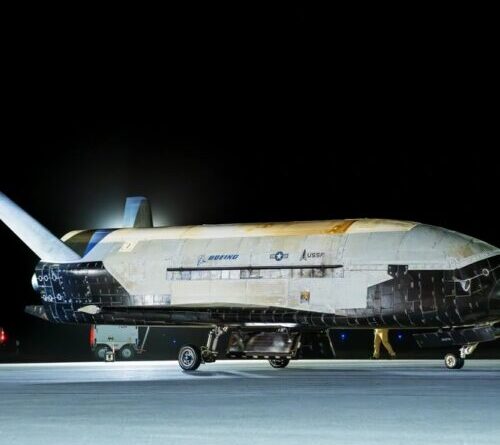
On this objective, military authorities stated the X-37B checked “space domain awareness technology experiments” that objective to enhance the Space Force’s understanding of the area environment. Defense authorities think about the area domain— like land, sea, and air—an objected to environment that might end up being a battleground in future disputes.
Last month, the Space Force launched the very first picture of Earth from an X-37B in area. This image was caught in 2024 as the spacecraft flew in its high-altitude orbit, and reveals a part of the X-37B’s power-generating solar selection.
Credit: United States Space Force
The Space Force hasn’t revealed prepare for the next X-37B objective. Generally, the next X-37B flight has actually introduced within a year of the previous objective’s landing. Far, all of the X-37B flights have actually released from Florida, with landings at Vandenberg and at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, where Boeing and the Space Force recondition the spaceplanes in between objectives.
The aerobraking maneuvers shown by the X-37B might discover applications on future functional military satellites, according to Gen. Stephen Whiting, head of United States Space Command.
“The X-37 is a test and experimentation platform, but that aerobraking maneuver allowed it to bridge multiple orbital regimes, and we think this is exactly the kind of maneuverability we’d like to see in future systems, which will unlock a whole new series of operational concepts,” Whiting stated in December at the Space Force Association’s Spacepower Conference.
Area Command’s “astrographic” location of obligation (AOR) begins at the top of Earth’s environment and encompasses the Moon and beyond.
“An irony of the space domain is that everything in our AOR is in motion, but rarely do we use maneuver as a way to gain positional advantage,” Whiting stated. “We believe at US Space Command it is vital, given the threats we now see in novel orbits that are hard for us to get to, as well as the fact that the Chinese have been testing on-orbit refueling capability, that we need some kind of sustained space maneuver.”
Improvements in maneuverability would have advantages in surveilling an enemy’s satellites, along with in protective and offending battle operations in orbit.
The Space Force might achieve the ability for continual maneuvers— understood in some quarters as vibrant area operations– in a number of methods. One is to use in-orbit refueling that permits satellites to “maneuver without regret,” and another is to pursue more fuel-efficient methods of altering orbits, such as aerobraking or solar-electric propulsion.
Whiting stated Space Command might change how it runs by using “maneuver warfare” as the Army, Navy and Air Force do. “We think we need to move toward a joint function of true maneuver advantage in space.”
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.