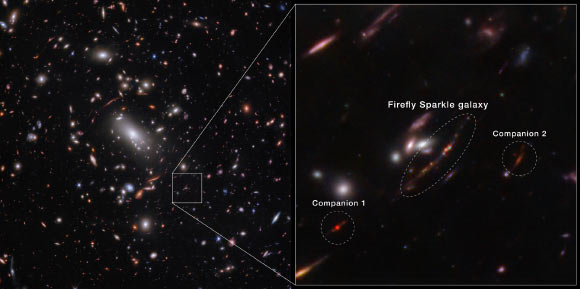
Nicknamed the Firefly Sparkle, the newly-discovered galaxy existed around 600 million years after the Big Bang and included a least 10 star clusters.
The Firefly Sparkle galaxy remains in the procedure of putting together and forming brand-new stars, existed about 600 million years after the Big Bang, and weighs about the like our Milky Way Galaxy if we might wind back the clock to see our Galaxy as it established. Image credit: NASA/ ESA/ CSA/ STScI/ C. Willott, NRC-Canada/ L. Mowla, Wellesley College/ K. Iyer, Columbia.
The most far-off galaxies identified are from when deep space was around 5% of its existing age.
These galaxies are around 10,000 times less enormous than the Milky Way and their low mass makes them challenging to observe.
The Firefly Sparkle galaxy was very first observed with the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, however brand-new comprehensive observations from the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope shed more light on the galaxy’s development.
“I didn’t believe it would be possible to solve a galaxy that existed so early in deep space into a lot of unique parts, not to mention discover that its mass resembles our own Galaxy’s when it remained in the procedure of forming,” stated Dr. Lamiya Mowla, an astronomer at Wellesley College.
“There is a lot going on inside this small galaxy, consisting of numerous various stages of star development.”
Webb had the ability to image the Firefly Sparkle galaxy in enough information for 2 factors.
One is an advantage of the universes: a huge foreground galaxy cluster called MACS J1423.8 +2404 significantly improved the remote galaxy’s look through a natural result referred to as gravitational lensing.
And when integrated with the telescope’s expertise in high-resolution imaging of infrared light, Webb provided unmatched brand-new information about the galaxy’s contents.
“Without the advantage of this gravitational lens, we would not have the ability to fix this galaxy,” stated Dr. Kartheik Iyer, an astronomer at Columbia University.
“We understood to anticipate it based upon existing physics, however it’s unexpected that we really saw it.”
The astronomers likewise observed 2 surrounding galaxies, which they call Firefly-Best Friend and Firefly-New Best Friend, situated at 6,000 and 40,000 light-years from Firefly Sparkle, respectively, less than the size of today day Milky Way.
Firefly Sparkle might be a young, gas-rich galaxy in its early development phase, the authors propose.
They show the mass of Firefly Sparkle is focused in 10 clusters of stars, with an overall mass of around 10 million times the mass of the Sun.
This makes Firefly Sparkle among the lowest-mass galaxies dealt with into star clusters observed at cosmic dawn, a date when galaxies were beginning to form, with a mass comparable to that of a progenitor Milky Way.
“It has actually long been forecasted that galaxies in the early Universe kind through succeeding interactions and mergers with other tinier galaxies,” stated Yoshihisa Asada, a doctoral trainee at Kyoto University.
“We may be experiencing this procedure in action.”
“This is simply the very first of numerous such galaxies Webb will find, as we are just beginning to utilize these cosmic microscopic lens,” stated Dr. Maruša Bradač, an astronomer at the University of Ljubljana.
“Just like microscopic lens let us see pollen grains from plants, the extraordinary resolution of Webb and the magnifying power of gravitational lensing let us see the little pieces inside galaxies.”
“Our group is now evaluating all early galaxies, and the outcomes are all pointing in the exact same instructions: we have yet to discover a lot more about how those early galaxies formed.”
The research study was released in the journal Nature
_____
L. Mowla et al2024. Development of a low-mass galaxy from star clusters in a 600-million-year-old Universe. Nature 636, 332-336; doi: 10.1038/ s41586-024-08293-0
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.