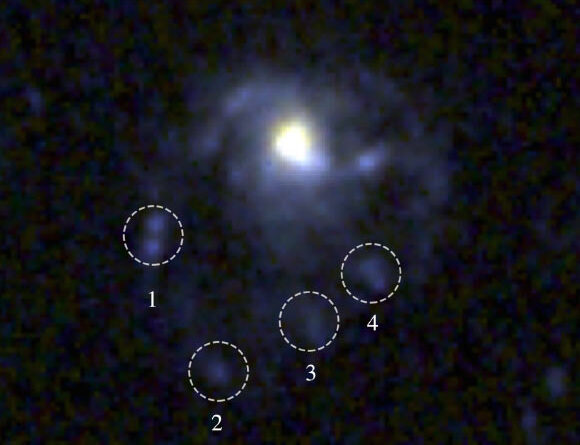
Utilizing the Near-Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph (NIRISS) instrument on the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope, astronomers have actually found 6 brand-new free-floating planetary-mass members of NGC 1333 with approximated masses in between 5 and 15 times the mass of Jupiter. Among these things, at 5 Jupiter masses (about 1,600 Earths), is a great prospect to be the most affordable mass things understood to have a dirty circumplanetary disk.
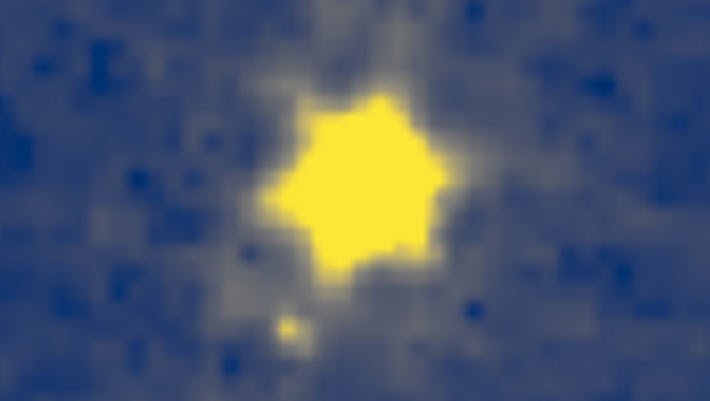
At an approximated mass of 5 Jupiter masses, NIRISS-NGC1333-5 (likewise called NN5) is a great prospect to be the lowest-mass item discovered in NGC 1333 so far and the lowest-mass things with a disk in any area recognized to date. Image credit: Langeveld et aldoi: 10.3847/ 1538-3881/ ad6f0c.
NGC 1333 is a star-forming cluster found some 1,000 light-years away in the northern constellation of Perseus.
Understood as Ced 16 and LBN 741, the cluster was very first found by the German astronomer Eduard Schönfeld in 1855.
Just 1-3 million years of ages, NGC 1333 hosts about half as lots of brown overshadows as stars, a greater percentage than seen before.
“We are penetrating the extremely limitations of the star forming procedure,” stated Johns Hopkins University astrophysicist Adam Langeveld.
“If you have an item that appears like a young Jupiter, is it possible that it could have ended up being a star under the ideal conditions? This is essential context for comprehending both star and world development.”
Dr. Langeveld and his coworkers performed an exceptionally deep spectroscopic study of NGC 1333 utilizing Webb’s NIRISS instrument.
The observations exposed 19 recognized brown overshadows and 6 free-floating planetary-mass things in between 5 and 10 times more huge than Jupiter.
That indicates they are amongst the lowest-mass items ever discovered to have actually grown from a procedure that would normally produce stars and brown overshadows, items straddling the limit in between stars and worlds that never ever fire up hydrogen blend and fade gradually.
“We utilized Webb’s extraordinary level of sensitivity at infrared wavelengths to look for the faintest members of a young star cluster, looking for to attend to an essential concern in astronomy: how light an item can form like a star?” stated Johns Hopkins University astrophysicist Ray Jayawardhana.
“It ends up the tiniest free-floating things that form like stars overlap in mass with huge exoplanets circling around neighboring stars.”
The Webb observations exposed no items lower than 5 Jupiter masses in spite of having enough level of sensitivity to discover such bodies.
That’s a strong sign that any outstanding items lighter than this limit are most likely to form the method worlds do.
“Our observations verify that nature produces planetary mass items in a minimum of 2 various methods– from the contraction of a cloud of gas and dust, the method stars kind, and in disks of gas and dust around young stars, as Jupiter in our own Solar System did,” Dr. Jayawardhana stated.
The most interesting of the planetary-mass things, NIRISS-NGC1333-5, is likewise the lightest, having actually an approximated mass of 5 Jupiters.
“The existence of a dirty disk indicates the item probably formed like a star, as area dust normally spins around a main item in the early phases of star development,” Dr. Langeveld stated.
“Disks are likewise a requirement for the development of worlds, recommending the observations might likewise have essential ramifications for possible mini worlds.”
“Those small items with masses equivalent to huge worlds might themselves have the ability to form their own worlds,” stated Dr. Aleks Scholz, an astrophysicist at the University of St Andrews.
“This may be a nursery of a mini planetary system, on a scale much smaller sized than our Solar System.”
The astronomers likewise found a brand-new brown dwarf with a planetary-mass buddy, an uncommon finding that difficulties theories of how double stars form.
“It’s most likely that such a set formed the method binary star systems do, from a cloud fragmenting as it contracted,” Dr. Jayawardhana stated.
“The variety of systems that nature has actually produced is exceptional and presses us to improve our designs of star and world development.”
The findings will be released in the Huge Journal
_____
Adam B. Langeveld et al2024. The JWST/NIRISS Deep Spectroscopic Survey for Young Brown Dwarfs and Free-Floating Planets. AJin press; doi: 10.3847/ 1538-3881/ ad6f0c
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.