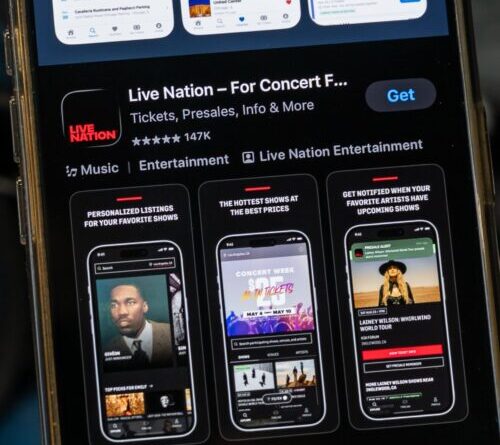
(Image credit: NASA/Aqua)
FAST FACTS
Where is it? Scotia Sea, South Atlantic Ocean [-54.4957805, -37.7561759]
What’s in the picture? Iceberg A23a, which is starting to disintegrate together with South Georgia island
Which satellite took the image? NASA’s Aqua satellite
When was it taken? May 3, 2025
A striking brand-new satellite image has actually exposed that the world’s biggest iceberg is beginning to disintegrate into countless smaller sized pieces as it stays stuck together with a wildlife haven in AntarcticaIt might take months, if not years, for the whole piece to vanish.
The “megaberg,” called A23a, presently has an area of around 1,200 square miles (3,100 square kilometers)– approximately the size of Long Island. It initially calved off of the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf in 1986, however it ended up being caught when its underside captured on the seafloor. It stayed stranded till January 2023, when it Started to move away from mainland AntarcticaThroughout this time, it has actually consistently held the title of “world’s largest iceberg” as larger bergs have actually reoccured, most just recently gaining back the title in June 2023
The huge iceberg ended up being caught once again in early 2024 after getting captured in a big ocean vortexIt stayed spinning on the area for a number of months before ultimately breaking complimentary in December 2024 and resuming its journey north through the Drake Passage — likewise referred to as the “iceberg graveyard,” where big Antarctic icebergs get swept away to their ultimate doom
In January, it ended up being clear that A23a was on a clash with South Georgia in the Scotia Sea. By March, the megaberg came to a stop as it grounded on the seafloor around 60 miles (100 kilometers) off the island’s southwest coast, where it ended up being caught for the 3rd– and most likely last– time in its prolonged life-span.
Now, pictures from NASA’s Aqua satellite have actually exposed that the edges of A23a are beginning to break down, particularly along its northern edge, blanketing the surrounding location with icy particles, according to NASA’s Earth Observatory “Thousands of iceberg pieces litter the ocean surface near the main berg, creating a scene reminiscent of a dark starry night,” NASA agents composed.
Related: See all the very best pictures of Earth from area
Smaller sized icebergs have actually been calving off A23a for months . This image was taken in January 2025, as the megaberg was making its last method towards South Georgia. (Image credit: Juergen Brand through Getty Images)
The various brand-new icebergs appear exceptionally little compared to A23a. “many measure at least a kilometer across and would pose a risk to ships,” NASA agents composed. The biggest piece to break off from the megaberg, which has actually been called A23c, has a location of around 50 square miles (130 square km) and is presently wandering south (simply out of the satellite image).
Get the world’s most interesting discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
This kind of iceberg disintegration is called “edge wasting” and has actually diminished A23a by around 200 square miles (520 square km) because it ended up being stuck in March, according to NASA. At this rate, it will likely take numerous months, if not years, for the berg to totally break apart, presuming bigger fractures do not rip it apart.
A23a might not hold its size title for long, due to the fact that as of May 16, it is just around 12 square miles (31 square km) bigger than the next-biggest iceberg, D15A, according to the U.S. National Ice Center
Wildlife sanctuary
South Georgia is not populated by individuals, aside from a couple of lots scientists who go to throughout the year. It is home to an abundance of wildlife, such as seals and seabirds, consisting of more than 2 million penguins, according to BirdLife International
Having a big iceberg moored simply offshore can be bothersome for these types, specifically for penguins that might need to take a trip numerous hundred additional miles around the blockage to reach their victim, depending upon where the iceberg lies. Meltwater originating from caught bergs can likewise change the temperature level and salinity of their environments
South Georgia is home to countless penguins, consisting of among the biggest nests of king penguins(Aptenodytes patagonicusworldwide. (Image credit: Getty Images)
It is presently uncertain just how much of an effect A23a is having on the regional wildlife. The iceberg is rather far off the coast, implying it will be less disruptive than it might have been. Some scientists have actually declared the melting piece might benefit the marine environment by launching nutrients into the ocean.
This is not the very first time that South Georgia has actually been put under siege by huge icebergs. In 2020, among the world’s previous biggest icebergs, A68, ended up being stuck even more detailed to the island, stimulating worries that it might interrupt penguin nestsUnlike A23a, it rapidly separated into lots of large portions after ocean currents ripped it in halftriggering it to rapidly dissolve and hence avoiding catastrophe.
As human-caused environment modification continues to trigger increased melting of Antarctica’s ice sheetsmuch more significant bergs might quickly go by South Georgia in the coming years.
Harry is a U.K.-based senior personnel author at Live Science. He studied marine biology at the University of Exeter before training to end up being a reporter. He covers a large range of subjects consisting of area expedition, planetary science, area weather condition, environment modification, animal habits and paleontology. His current deal with the solar optimum won “best space submission” at the 2024 Aerospace Media Awards and was shortlisted in the “top scoop” classification at the NCTJ Awards for Excellence in 2023. He likewise composes Live Science’s weekly Earth from area series.
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.