REBELS-25 existed as early as 700 million years after Big Bang, according to a paper released in the Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
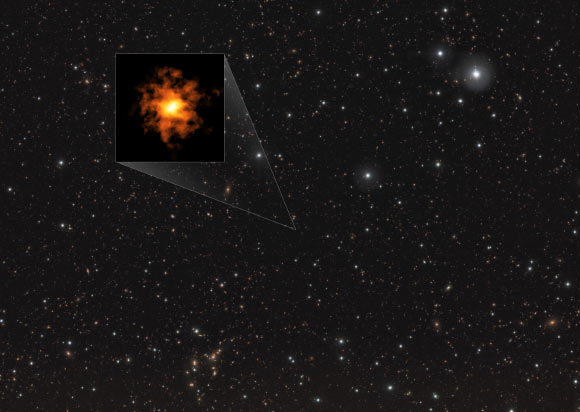
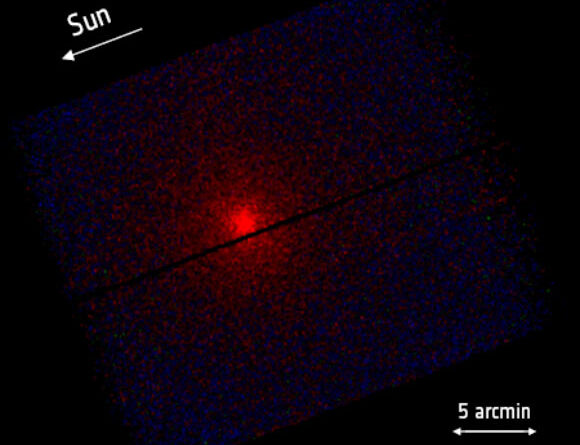
This image reveals the galaxy REBELS-25 as seen by ALMA, overlaid on an infrared picture of other stars and galaxies. The infrared image was taken by ESO’s Visible and Infrared Survey Telescope for Astronomy(VISTA). Image credit: ALMA/ ESO/ NAOJ/ NRAO/ Rowland et al/ Dunlop et al/ CASU/ CALET.
The galaxies we see today have actually come a long method from their disorderly, clumpy equivalents that astronomers normally observe in the early Universe.
These unpleasant, early galaxies combine with each other and after that develop into smoother shapes at an exceptionally sluggish rate.
Present theories recommend that, for a galaxy to be as organized as our own Milky Way– a turning disk with neat structures like spiral arms– billions of years of advancement need to have expired.
The detection of REBELS-25, nevertheless, difficulties that timescale.
“According to our understanding of galaxy development, we anticipate most early galaxies to be little and untidy looking,” stated Dr. Jacqueline Hodge, an astronomer at Leiden University.
In their research study, Dr. Hodge and coworkers discovered that REBELS-25 lives at redshift z=7.3 (when deep space was just 700 million years of ages), making it the most far-off highly turning disk galaxy ever found.
“Seeing a galaxy with such resemblances to our own Milky Way, that is highly rotation-dominated, challenges our understanding of how rapidly galaxies in the early Universe progress into the organized galaxies these days’s universes,” states Lucie Rowland, a doctoral trainee at Leiden University.
REBELS-25 was spotted by the authors utilizing the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA).
To correctly recognize the structure and movement of the galaxy, they carried out follow-up observations with ALMA at a greater resolution, which verified its record-breaking nature.
Remarkably, the information meant more industrialized functions comparable to those of the Milky Way, like a main lengthened bar, and even spiral arms, although more observations will be required to verify this.
“Finding additional proof of more developed structures would be an amazing discovery, as it would be the most remote galaxy with such structures observed to date,” Rowland stated.
“These future observations of REBELS-25, together with other discoveries of early turning galaxies, will possibly change our understanding of early galaxy development, and the development of deep space as a whole.”
_____
Lucie E. Rowland et alREBELS-25: Discovery of a dynamically cold disc galaxy at z=7.31. MNRASreleased online October 7, 2024; doi: 10.1093/ mnras/stae2217
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.