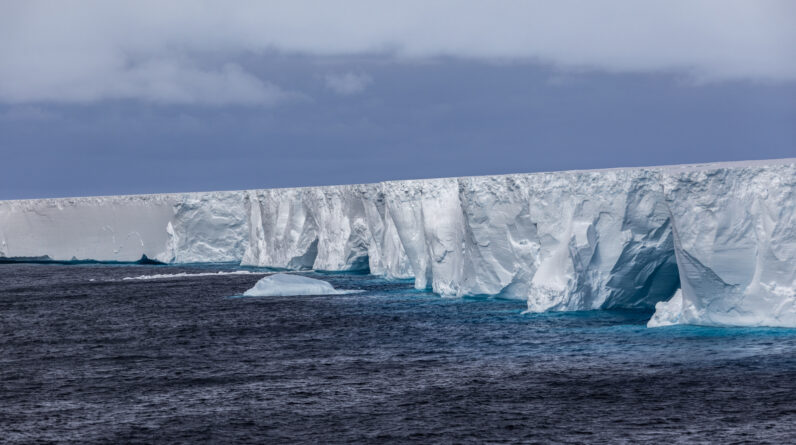
A23a is a massive iceberg with an area more than 3 times higher than New York City.
( Image credit: Samuel J Cole/Getty Images )
The world’s biggest iceberg is on the relocation once again after leaving from a huge vortex that triggered it to spin in location for months. This is the huge berg’s 2nd fantastic escape in as several years, after breaking devoid of the seafloor where it was stuck for 37 years in 2023.
Researchers are now carefully keeping an eye on the icy piece’s sluggish march towards oblivion in hopes of discovering more about the short-term covert environment it might support.
A23a, which is typically called a “megaberg,” has an area approximately 3 times bigger than New York City and weighs simply under 1 trillion loads. It initially broke off from Antarctica’s Filchner Ice Shelf in 1986 however ended up being caught on the seafloor simply a couple of miles offshore, which has considerably slowed its melt rate. Over the last couple of years, it has actually held the title of “world’s largest iceberg” on numerous celebrations, most just recently because May 2023, when the previous biggest berg– A-76A– disintegrated
Late in 2015, A23a Broke complimentary from its seafloor tether and started moving far from Antarctica. It didn’t get far. Simply a couple of months later on, the massive ice island got caught to the east of the South Orkney Islands in a Taylor column– a huge mass of turning water brought on by ocean currents circling around an undersea mountain, or seamount. At its optimum spin speed, the berg was turning about 15 degrees counterclockwise every day, scientists composed on YouTube
As of Dec. 13, the megaberg has actually gotten away from the Taylor column and resumed its journey away from the South Pole, according to a declaration by the British Antarctic Survey (BAS).
Related: ISS astronaut records constellation of icebergs in fantastic area pictures
A23a megaberg gets away after months in ocean vortex|British Antarctic Survey – YouTube
View On
“It’s exciting to see A23a on the move again after periods of being stuck,” Andrew Meijersan oceanographer at BAS, stated in the declaration.
“We are interested to see if it will take the same route the other large icebergs that have calved off Antarctica have taken. And more importantly what impact this will have on the local ecosystem.”Get the world’s most interesting discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
Get the world’s most interesting discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
Drake Passage, the ‘iceberg graveyard’
The majority of huge icebergs that break off from Antarctica drift north through an area of the Southern Ocean referred to as the Drake Passage, which has actually ended up being referred to as the “iceberg graveyard” due to the fact that it moves icebergs north into warmer waters, where they ultimately disintegrate.
This is what occurred to A-76A in 2015 and its predecessor A68a, which likewise travelled through this area before being ripped in half by ocean currents in 2020
This graphic demonstrate how A23a has actually slowly moved far from Antarctica and where it got stuck in the Taylor column(in the rectangle-shaped box). (Image credit: Omar Zaghloul/Anadolu through Getty Images utilizing information from the British Antarctic Survey)
Scientists are keeping an especially close eye on A23a for more information about how its ultimate break up might affect the surrounding ocean environment.
“We know that these giant icebergs can provide nutrients to the waters they pass through, creating thriving ecosystems in otherwise less productive areas,” Laura Taylora doctoral prospect in biogeochemistry with BAS, stated in the declaration. “What we don’t know is what difference particular icebergs, their scale, and their origins can make to that process.”
Researchers have actually taken water samples throughout the iceberg’s forecasted course and will continue to take samples in its wake. Comparing these samples with one another must assist clarify this secret.
Harry is a U.K.-based senior personnel author at Live Science. He studied marine biology at the University of Exeter before training to end up being a reporter. He covers a wide variety of subjects consisting of area expedition, planetary science, area weather condition, environment modification, animal habits and paleontology. His current deal with the solar optimum won “best space submission” at the 2024 Aerospace Media Awards and was shortlisted in the “top scoop” classification at the NCTJ Awards for Excellence in 2023. He likewise composes Live Science’s weekly Earth from area series.
A lot of Popular
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.