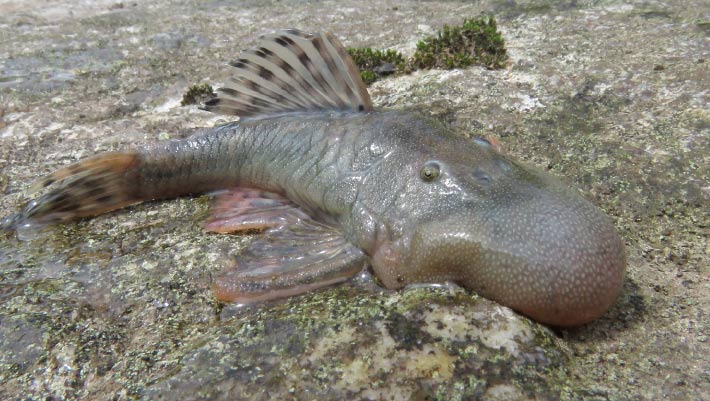
In 2022, biologists with Conservation International carried out a study that discovered a chest of biodiversity in the heart of the Alto Mayo landscape, which covers about 780,700 hectares (1.9 million acres) in the upper basin of the Mayo River, within the provinces of Moyobamba and Rioja, in Peru’s San Martín department. The study exposed a minimum of 27 brand-new types– consisting of a ‘blob-headed’ fish types of the bristlemouth armored catfish genus Chaetostoma — and 49 types that are threatened with termination according to the IUCN Red List.
The’blob-headed’bristlemouth armored catfish (Chaetostoma sp.). Image credit: Conservation International/ Robinson Olivera.
The Alto Mayo landscape, covering the Andes to the Amazon and consisting of the Alto Mayo Protected Forest, is a complicated mosaic of environments and neighborhoods, consisting of Indigenous areas, towns and cities.
Throughout the 38-day study, Conservation International scientists tape-recorded 2,046 types, highlighting the vital significance of saving the area.
A minimum of 34 of them appear to live just in the Alto Mayo landscape, consisting of the Andean saddle-back tamarin.
To record many types, the researchers matched standard study techniques with innovations such as video camera traps, bioacoustics sensing units and ecological DNA (eDNA) gathered from the water.
“Discovering 4 brand-new mammals in any exploration is unexpected– discovering them in an area with considerable human populations is remarkable,” stated Dr. Trond Larsen, who leads Conservation International’s Rapid Assessment Program in the Moore Center for Science.
“This is a lively, vibrant mosaic of environments, both natural and anthropogenic, that we should keep and bring back if we want to secure the types discovered there.”
Throughout the exploration, the biologists determined 68 types of fish throughout almost 30 research study locations.
Eighteen types were taped for the very first time in the Alto Mayo basin and another 8 were brand-new to science, consisting of undescribed types from the Characiformes group along with catfishes.
Amongst the stunning brand-new fish discoveries was a ‘blob-headed’ fish of the genus Chaetostoma
This types has a bigger blob-like head, a function that the group’s fish researchers had actually never ever seen before. The function of this uncommon structure stays a secret.
More than 200 types of butterflies were recognized throughout the study, consisting of 10 brand-new to science, 24 possibly brand-new to science (pending additional examination) and 14 tape-recorded in Alto Mayo for the very first time.
The scientists tape-recorded more than 70 types of scarab beetles throughout Alto Mayo’s varied environments, consisting of 2 types of Scybalocanthon that are brand-new to science and 45 types formerly undocumented in the area.
They recorded an impressive 536 bird types throughout a series of elevations and a range of environments consisting of cloud forests, lowland forests, palm swamps and coffee plantations.
They likewise recorded 27 types of amphibians and 18 types of reptiles– more than anticipated provided prior keeping track of in the area and the distance of human settlements to a number of the research study locations.
They discovered 3 types of amphibians brand-new to science– a climbing up salamander (Bolitoglossa sp.), and 2 frogs (Chiasmocleis sp. and Pristimantis sp.)– along with 7 more types that are most likely brand-new however need more examination.
2 snake types were found that are possibly brand-new to science– Atractus sp. and a below ground blind snake from the genus Epictia
Utilizing a mix of techniques that consists of video camera traps, the group tape-recorded 50 types of medium and big mammals (over 1 kg) throughout a variety of elevation and environment types.
Omitting bats, the scientists recognized 35 types of little, non-flying mammals (little rodents and marsupials, less than 1 kg), 12 of which were recorded in the Alto Mayo landscape for the very first time.
In addition to them, another 45 types of bats were tape-recorded throughout the research study, consisting of a brand-new types of the Carollia genus– short-tailed fruit bats.
The exploration likewise recorded over 950 types of vascular plants in main Alto Mayo, consisting of 5 types endemic to the San Martín area and 10 noted as threatened with termination by the IUCN Red List.
Amongst the discoveries were 3 types possibly brand-new to science– Stylogyne sp., Ilex sp. and Schefflera sp.– which are going through additional research study.
“We discovered that locations closer to cities and towns still support exceptionally high biodiversity, consisting of types discovered no place else,” Dr. Larsen stated.
“These findings highlight that even in locations greatly affected by individuals, biodiversity can continue however just if communities are handled sustainably.”
“The more thorough understanding of where types live assists us recognize locations with the best capacity for saving or bring back biodiversity, along with those finest fit for sustainable activities like ecotourism, selective logging, farming and resource harvesting,” he included.
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.