Called 2017 OF201, the newly-discovered trans-Neptunian item is among the most far-off noticeable things in our Solar System and is most likely big (about 700 km in size) enough to certify as a dwarf world.
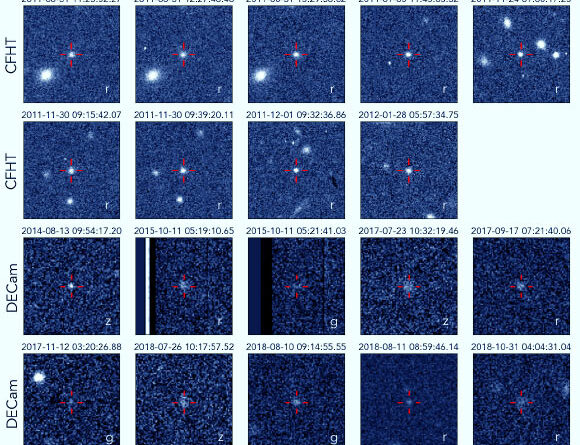
Cutout pictures of all 19 detections of 2017 OF201. Image credit: Cheng et alarXiv: 2505.15806.
Trans-Neptunian things( TNOs)are small worlds that orbit the Sun at a higher average range than the orbit of Neptune.
After 30 years of the discovery of the very first TNOs besides Pluto, different study programs have actually been carried out to check out the huge area of the external Solar System, and more than 5,000 TNOs have actually been found up until now.
The newly-discovered TNO is unique for 2 factors: its severe orbit and its plus size.
“The item’s aphelion– the farthest point on the orbit from the Sun– is more than 1,600 times that of the Earth’s orbit,” stated Dr. Sihao Cheng, an astronomer at the Institute for Advanced Study and Perimeter Institute.
“Meanwhile, its perihelion– the closest point on its orbit to the Sun– is 44.5 times that of the Earth’s orbit, comparable to Pluto’s orbit.”
“This severe orbit, which takes the item around 25,000 years to finish, recommends a complicated history of gravitational interactions.”
“It should have experienced close encounters with a huge world, triggering it to be ejected to a broad orbit,” included Princeton University astronomer Dr. Eritas Yang.
“There might have been more than one action in its migration.”
“It’s possible that this item was very first ejected to the Oort cloud, the most remote area in our Solar System, which is home to lots of comets, and after that returned.”
“Many severe TNOs have orbits that appear to cluster in particular orientations, however 2017 OF201 differs this,” stated Dr. Jiaxuan Li, likewise from Princeton University.
“This clustering has actually been analyzed as indirect proof for the presence of another world in the Solar System, Planet X or Planet Nine, which might be gravitationally shepherding these things into their observed patterns.”
“The presence of 2017 OF201 as an outlier to such clustering might possibly challenge this hypothesis.”
The astronomers approximate 2017 OF201’s size to be 700 km, which would make it the second biggest recognized things in such a broad orbit.
“2017 OF201 invests just 1% of its orbital time close enough to us to be noticeable,” Dr. Cheng stated.
“The existence of this single item recommends that there might be another hundred or two other items with comparable orbit and size; they are simply too far to be noticeable now.”
The scientists found 2017 OF201 as part of a continuous research study task to determine TNOs and possible brand-new worlds in the external Solar System.
The item was recognized by determining intense areas in a huge image database from the Victor M. Blanco Telescope and Canada France Hawaii Telescope (CFHT), and attempting to link all possible groups of such areas that appeared to cross the sky in the method a single TNO might.
The researchers determined 2017 OF201 in 19 various direct exposures, caught over 7 years.
“Even though advances in telescopes have actually allowed us to check out far-off parts of deep space, there is still a good deal to find about our own Solar System,” Dr. Cheng stated.
The group’s paper was published online on arXiv.org
_____
Sihao Cheng et al2025. Discovery of a dwarf world prospect in an incredibly broad orbit: 2017 OF201. arXiv: 2505.15806
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.