Physicists with the CMS Collaboration at CERN’s Large Hadron Collider have actually evaluated whether leading quarks stick to Albert Einstein’s unique theory of relativity.
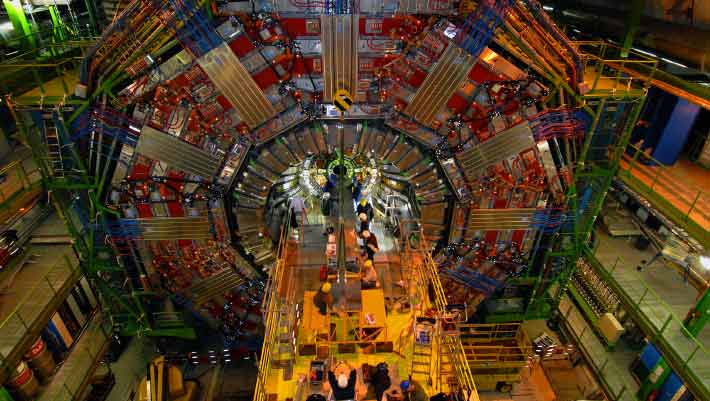
Setup of the CMS beam pipeline. Image credit: CERN/ CMS Collaboration.
Together with quantum mechanics, Albert Einstein’s unique theory of relativity functions as the basis of the Standard Model of particle physics.
At its heart is a principle called Lorentz proportion: speculative outcomes are independent of the orientation or the speed of the try out which they are taken.
Unique relativity has actually stood the test of time. Some theories, consisting of specific designs of string theory, anticipate that, at really high energies, unique relativity will no longer work and speculative observations will depend on the orientation of the experiment in space-time.
Residues of such Lorentz proportion breaking might be observable at lower energies, such as at the energies of the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), however regardless of previous efforts, they have actually not been discovered at the LHC or other colliders.
In a brand-new research study, the CMS physicists looked for Lorentz proportion breaking at the LHC utilizing sets of leading quarks– the most huge primary particles understood.
“In this case, a reliance on the orientation of the experiment would indicate that the rate at which top-quark sets are produced in proton-proton accidents at the LHC would differ with time,” they stated.
“More specifically, because Earth turns around its axis, the instructions of the LHC proton beams and the typical instructions of leading quarks produced in crashes at the centre of the CMS experiment likewise alter depending upon the time of the day.”
“As an effect, and if there is a preferential instructions in space-time, the top-quark-pair production rate would differ with the time of the day.”
“Hence, discovering a discrepancy from a continuous rate would total up to finding a preferential instructions in space-time.”
The group’s brand-new outcome, which is based upon information from the 2nd run of the LHC, concurs with a continuous rate, implying that Lorentz proportion is not broken and Einstein’s unique relativity stays legitimate.
The scientists utilized the outcome to set limitations on the magnitude of criteria that are forecasted to be null when the balance holds.
The limitations acquired enhance by as much as an element of 100 upon arise from a previous look for Lorentz proportion breaking at the previous Tevatron accelerator.
“The outcomes lead the way for future look for Lorentz proportion breaking based upon top-quark information from the 3rd run of the LHC,” the researchers stated.
“They likewise unlock to analysis of procedures including other heavy particles that can just be examined at the LHC, such as the Higgs boson and the W and Z bosons.”
The research study was released in the October 2024 problem of the journal Physics Letters B
_____
CMS Collaboration. 2024. Look for infraction of Lorentz invariance in leading quark set production utilizing dilepton occasions in 13 TeV proton-proton crashes. Physics Letters B 857: 138979; doi: 10.1016/ j.physletb.2024.138979
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.