Introduced on December 19, 2013, the fuel tank of ESA’s star-mapping satellite Gaia is now approaching empty, however this is far from completion of the objective. Innovation tests are set up for the weeks ahead before Gaia is transferred to its ‘retirement’ orbit, and 2 huge information releases are tabled for around 2026 and completion of this years, respectively.
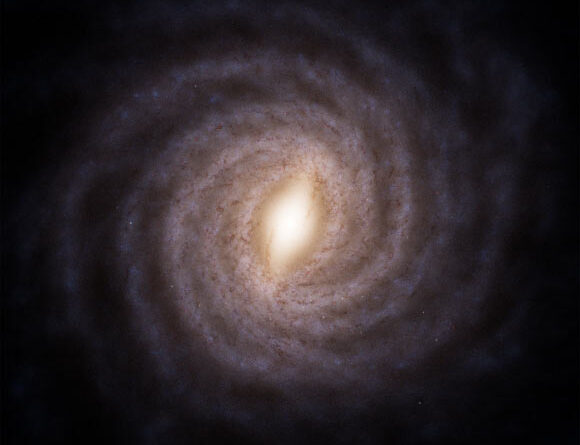
An artist’s impression of the Milky Way Galaxy, based upon information from ESA’s Gaia area telescope. Image credit: ESA/ Gaia/ DPAC/ Stefan Payne-Wardenaar.
“Today marks completion of science observations and we are commemorating this amazing objective that has actually surpassed all our expectations, lasting for nearly two times its initially visualized life time,”stated ESA Director of Science Carole Mundell.
“The bonanza of information gathered by Gaia has actually provided us distinct insights into the origin and development of our Milky Way Galaxy, and has actually likewise changed astrophysics and Solar System science in manner ins which we are yet to totally value.”
“Gaia constructed on distinct European quality in astrometry and will leave a lasting tradition for future generations.”
“After 11 years in area and enduring micrometeorite effects and solar storms along the method, Gaia has actually ended up gathering science information,” stated Gaia task researcher Johannes Sahlmann.
“Now all eyes turn towards the preparation of the next information releases.”
“I am delighted with the efficiency of this extraordinary objective, and thrilled about the discoveries that await us.”
An artist’s impression(annotated)of the Milky Way Galaxy, based upon information from ESA’s Gaia area telescope. Image credit: ESA/ Gaia/ DPAC/ Stefan Payne-Wardenaar.
Gaia has actually been charting the positions, ranges, motions, brightness modifications, structure and various other attributes of stars by monitoring them with its 3 instruments often times throughout the objective.
This has actually made it possible for Gaia to provide on its main objective of constructing the biggest, most exact map of the Milky Way, revealing us our home Galaxy like no other objective has actually done in the past.
“It includes significant modifications from previous designs, due to the fact that Gaia has actually altered our impression of the Milky Way,” stated Stefan Payne-Wardenaar, clinical visualizer for the Haus der Astronomie and the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education.
“Even standard concepts have actually been modified, such as the rotation of our Galaxy’s main bar, the warp of the disc, the in-depth structure of spiral arms, and interstellar dust near the Sun.”
“Still, the remote parts of the Milky Way stay informed guesses based upon insufficient information.”
“With additional Gaia information launches our view of the Milky Way will end up being much more precise.”
The Gaia clinical and engineering groups are currently working complete steam on the preparations for Gaia Data Release 4 (DR4), anticipated in 2026.
The information volume and quality enhances with every release and Gaia DR4, with an anticipated 500 TB of information items, is no exception.
It will cover the objective’s very first 5.5 years, corresponding to the length of the initially predicted period of the objective.
“This is the Gaia release the neighborhood has actually been waiting on, and it’s amazing to believe this just covers half of the gathered information,” stated Dr. Antonella Vallenari, an astronomer at the Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica.
“Even though the objective has actually now stopped gathering information, it will be service as normal for us for several years to come as we make these amazing datasets all set for usage.”
Gaia has actually finished the sky-scanning stage of its objective, acquiring more than 3 trillion observations of about 2 billion stars and other items over the last years to change our view of our home Galaxy and cosmic community. Image credit: ESA/ Gaia/ DPAC/ Stefan Payne-Wardenaar.
After numerous weeks of screening, Gaia will leave its present orbit around Lagrange point 2, 1.5 million km from the Earth in the instructions far from the Sun, to be taken into its last heliocentric orbit, far from Earth’s sphere of impact.
The spacecraft will be passivated on March 27, 2025, to prevent any damage or disturbance with other spacecraft.
Throughout the innovation evaluates Gaia’s orientation will be altered, indicating it will briefly end up being numerous magnitudes brighter, making observations through little telescopes a lot much easier.
“Gaia will treat us with this last present as we bid goodbye, shining amongst the stars ahead of its well-earned retirement,” stated Gaia objective supervisor Uwe Lammers.
“It’s a minute to commemorate this transformative objective and thank all of the groups for more than a years of effort running Gaia, preparing its observations, and guaranteeing its valuable information are returned efficiently to Earth.”
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.