 >
>
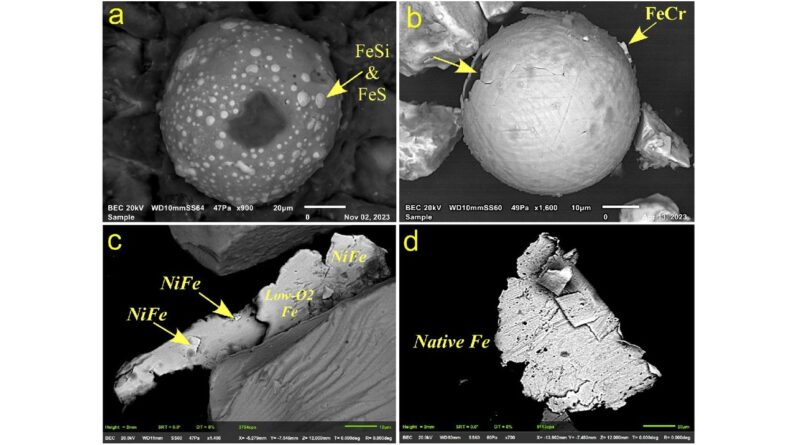
(Image credit: Moore et al., 2025, PLOS One, CC-BY 4.0 )
Researchers have actually discovered brand-new proof that a huge comet path might have triggered environment turmoil in the world more than 12,000 years back.
Tiny particles spotted in ocean sediment cores recommend that dust from a big, breaking down comet went into Earth’s environment around the start of the Younger Dryas occasion, a duration of abrupt cooling that triggered temperature levels in the Northern Hemisphere to plunge by as much as 18 degrees Fahrenheit (10 degrees Celsius) within about a year. The scientists shared their findings Aug. 6 in the journal PLOS One
“The amount of comet dust in the atmosphere was enough to cause a short-term ‘impact winter,'” which resulted in a prolonged duration of cooling, research study co-author Vladimir Tselmovichan Earth researcher at Borok Geophysical Observatory in Russia, stated in a declarationAfter 7,000 years of progressive warming, Earth experienced a duration of quick cooling about 12,900 years earlier. Called the Younger Dryas, after the wildflowers of the Dryas genus that grew in cooler temperature levels, this chillier period lasted about 1,200 years before warming resumed.
Completing hypotheses explain what began the Younger Dryas. Many researchers believe cold freshwater lakes put into oceans as Earth’s glaciers melted, and this deteriorated massive ocean currents that brought warm water northward from the tropics. Others have actually proposed that effects from a breaking down comet filled the environment with dust and destabilized the world’s ice sheets, setting off long-lasting cooling.
No one has actually discovered proof of an effect crater dated to the start of the Younger Dryas that might have set off such an occasion. What’s more, some researchers declare that a few of the expected proof for the hypothesis– such as “black mats” which contain metals typical to asteroids from around the start of the Younger Dryas– might rather be discussed by more ordinary procedures.
Related: The Gulf Stream stopped pumping nutrients throughout the last glacial epoch– and the exact same might be taking place now
Get the world’s most remarkable discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
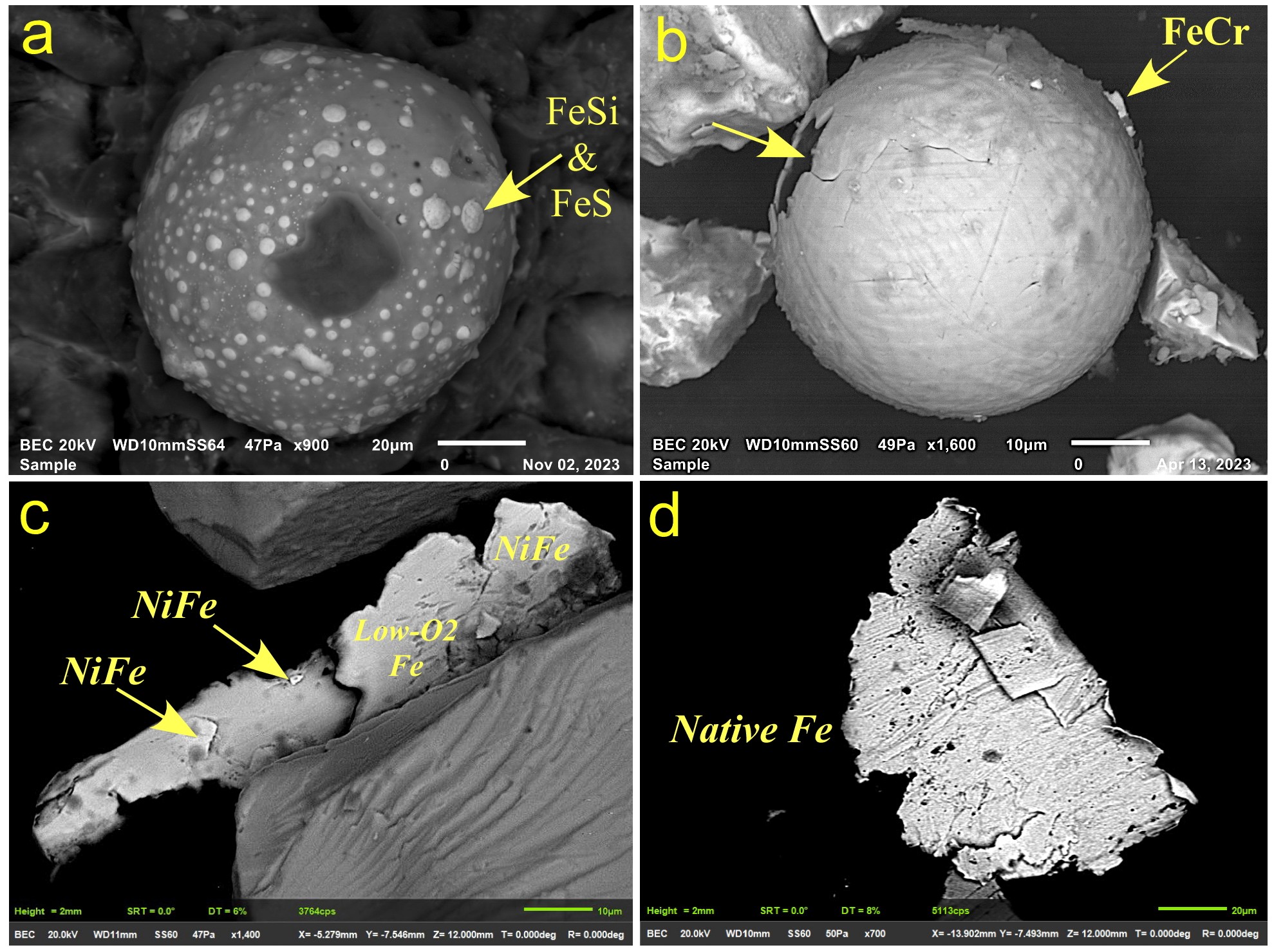
In the brand-new research study, scientists studied ocean sediment cores from Baffin Bay, in between Greenland and Canada, to look for proof of a possible effect. The group discovered small metal particles that might have originated from comet dust, in addition to even smaller sized particles with high levels of platinum and iridium, components that prevail in comets and meteorites.
They likewise discovered tiny round particles that probably formed on Earth however might consist of percentages of product from a comet or asteroid. All of these appeared around the time the Younger Dryas started.
The brand-new research study does not straight validate the effect hypothesis. Rather, the particles function as indirect proof of an effect or “airburst,” which takes place when a meteor blows up inside a world’s environment before striking the ground.
These effects may have originated from a big, breaking down comet that later on triggered Comet Encke and the Taurid Complex, the source of the yearly Taurid meteor shower, the scientists composed in the research study.
More research study is required to verify this proposition. The group prepares to check other ocean cores for comparable particles to verify whether the Younger Dryas started soon after those particles appear in the geological record.
Skyler Ware is a freelance science reporter covering chemistry, biology, paleontology and Earth science. She was a 2023 AAAS Mass Media Science and Engineering Fellow at Science News. Her work has actually likewise appeared in Science News Explores, ZME Science and Chembites, to name a few. Skyler has a Ph.D. in chemistry from Caltech.
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.