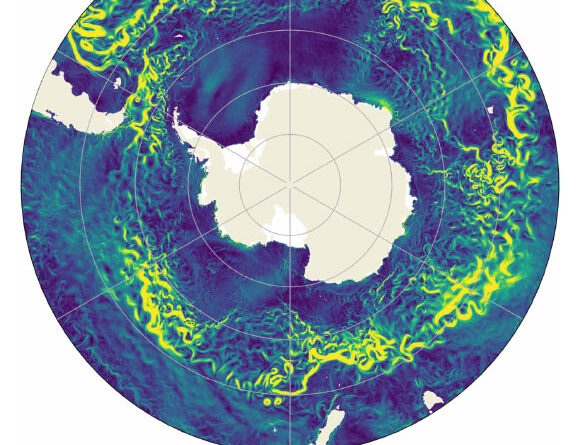
More than 4 times more powerful than the Gulf Stream, the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) is the world’s greatest ocean present and plays an out of proportion function in the environment system due to its function as an avenue for significant ocean basins. Researchers from the University of Melbourne and NORCE Norway Research Centre have actually now revealed the ACC slowing down by around 20% by 2050 in a high carbon emissions circumstance. This increase of fresh water into the Southern Ocean is anticipated to alter the homes, such as density (salinity), of the ocean and its flow patterns.
Sohail et alexamined a high-resolution ocean and sea ice simulation of ocean currents, heat transportation and other aspects to identify the effect of altering temperature level, saltiness and wind conditions. Image credit: Sohail et aldoi: 10.1088/ 1748-9326/ adb31c.
“The ocean is incredibly complicated and carefully well balanced,”stated research study co-author Dr. Bishakhdatta Gayen, a fluid mechanist at the University of Melbourne.
“If this present ‘engine’ breaks down, there might be serious effects, consisting of more environment irregularity, with higher extremes in specific areas, and sped up worldwide warming due to a decrease in the ocean’s capability to function as a carbon sink.”
The ACC works as a barrier to intrusive types, like rafts of southern bull kelp that ride the currents, or marine-borne animals like shrimp or mollusks, from other continents reaching Antarctica.
As this present slows and compromises, there is a greater possibility such types will make their method onto the delicate Antarctic continent, with a possibly extreme influence on the food web, which may, for instance, alter the readily available diet plan of Antarctic penguins.
The ACC is an important part of the world’s ocean conveyor belt, which moves water around the world– connecting the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans– and is the primary system for the exchange of heat, co2, chemicals and biology throughout these ocean basins.
In their research study, the authors utilized Australia’s fastest supercomputer and environment simulator, GADI, situated at Access National Research Infrastructure.
They discovered that the transportation of ocean water from the surface area to the deep might likewise slow in the future.
“It is anticipated that the slow-down will be comparable under the lower emissions situation, offered ice melting speeds up as forecasted in other research studies,” Dr. Sohail stated.
“The 2015 Paris Agreement intended to restrict worldwide warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.”
“Many researchers concur that we have actually currently reached this 1.5 degree target, and it is most likely to get hotter, with flow-on effect on Antarctic ice melting.”
“Concerted efforts to restrict international warming (by minimizing carbon emissions) will restrict Antarctic ice melting, preventing the forecasted ACC downturn.”
The research study exposes that the effect of ice melting and ocean warming on the ACC is more intricate than formerly believed.
“The melting ice sheets discard large amounts of fresh water into the salted ocean,”
“This abrupt modification in ocean salinity has a series of repercussions– consisting of the weakening of the sinking of surface area ocean water to the deep (called the Antarctic Bottom Water), and, based upon this research study, a weakening of the strong ocean jet that surrounds Antarctica,” Dr. Gayen stated.
The research study was released in the journal Environmental Research Letters
_____
Taimoor Sohail et al2025. Decrease of Antarctic Circumpolar Current due to polar ocean freshening. Environ. Res. Lett 20, 034046; doi: 10.1088/ 1748-9326/ adb31c
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.