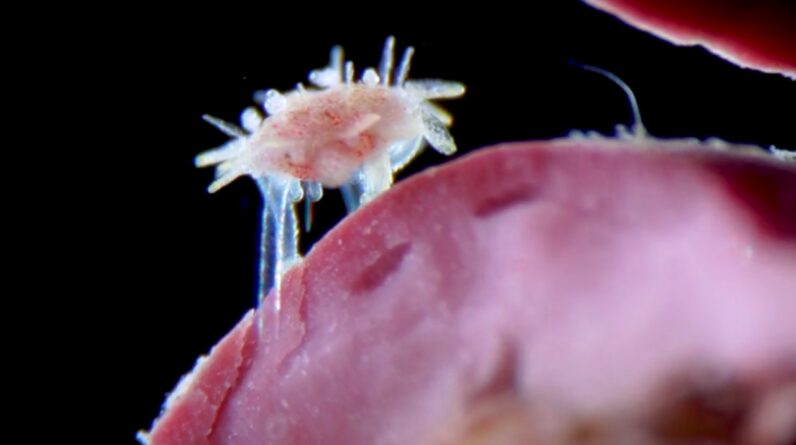
Stunning tiny video footage has actually recorded the minute a clear child sea urchin crawled throughout a bed of red algae. The video made 5th location in the yearly Nikon Small World in Motion competitors.
Alvaro Migottoa zoologist at the University of São Paulo in Brazil, recorded the enchanting video of the juvenile sea urchin as it crossed its environment and determined the types as Arbacia lixula — a black sea urchin that is frequently discovered along the Brazilian coast and throughout the Mediterranean. Migotto found the small animal while analyzing particles that had actually cleaned ashore near the Center for Marine Biology where he works.
“It was simply by chance. While I was examining various materials — such as algae, pebbles, and seashells washed ashore — under the stereomicroscope in search of other organisms, I unexpectedly came across this tiny sea urchin calmly walking on a piece of red calcareous algae,” Migotto informed Live Science in an e-mail.”The scene struck me as perfect — not only was the animal moving naturally over a substrate it typically inhabits in the wild, but the combination of these two elements also created excellent contrast and pleasing colors,” he included.
Associated link: How to picture your microscopic lense specimens
Sea urchins are marine invertebrates in the group Echinodermata and are discovered in oceans all over the world and in almost every environment. They have round, spiny bodies and numerous small tubed feet.
Nikon revealed the winners and respectable points out of the competitors on Sept. 24.
Get the world’s most remarkable discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
The leading reward went to microscopist Jay McClellan for his time-lapse video recording the self-pollination of a thyme-leaved speedwell (Veronica serpyllifolia. Professional photographer Benedikt Pleyer was granted 2nd location for a swarm of Volvox algae in the main hole of a Japanese 50-yen coin.
Other notable discusses consist of an 18-hour timelapse recording the development of a chick’s sensory nerve cells, a 3D composite of a male dung beetle (Sulcophanaeus imperatordeveloped from more than 7,000 images and a recording of mitochondria and calcium waves in the muscle cells of a contracting human heart.
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.