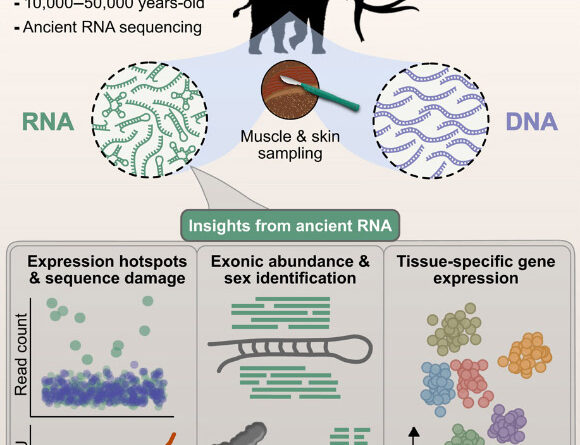
Researchers have actually effectively drawn out and sequenced ancient RNA from permafrost-preserved tissues of 10 woolly mammoths. Among these, dated to be 39,000 years of ages, represents the earliest ancient RNA series tape-recorded to date.
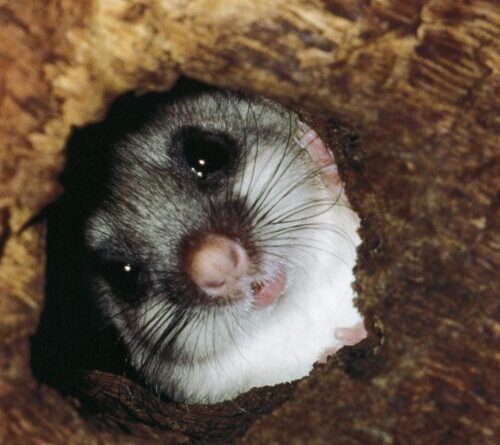
Mármol-Sánchez et aldiscovered ancient RNA particles in Late Pleistocene woolly massive tissues. Image credit: Mármol-Sánchez et aldoi: 10.1016/ j.cell.2025.10.025.
Sequencing ancient genes and studying how they are triggered is necessary to comprehend the biology and advancement of extinct types.
For many years, researchers have actually been deciphering massive DNA to piece together their genomes and evolutionary history.
RNA, the particle that reveals which genes are active, has actually so far stayed out of reach.
“With RNA, we can get direct proof of which genes are ‘switched on,’ using a glance into the last minutes of life of a massive that strolled the Earth throughout the last Ice Age,” stated Dr. Emilio Mármol, a scientist at the Globe Institute.
“This is details that can not be gotten from DNA alone.”
For the research study, Dr. Mármol and associates gathered permafrost-preserved tissues from 10 woolly mammoths dated to the Late Pleistocene and discovered in northeastern Siberian paleontological fields extending from the Central Indigirka area to the mainland Oyogos Yar coast and the New Siberian Islands.
“We got to incredibly unspoiled massive tissues uncovered from the Siberian permafrost, which we hoped would still include RNA particles frozen in time,” Dr. Mármol stated.
“We have actually formerly pressed the limitations of DNA healing past a million years,” stated Professor Love Dalén, a scientist at Stockholm University and the Centre for Palaeogenetics.
“Now, we wished to check out whether we might broaden RNA sequencing even more back in time than performed in previous research studies.”
The scientists had the ability to determine tissue-specific patterns of gene expression in the 39,000-year-old muscle stays from the juvenile massive Yuka.
Amongst the more than 20,000 protein-coding genes in the massive’s genome, far from all of them were active.
The found RNA particles code for proteins with crucial functions in contraction and metabolic policy under tension.
The researchers likewise discovered a myriad of RNA particles that manage the activity of genes in the massive muscle samples.
“RNAs that do not encode for proteins, such as microRNAs, were amongst the most interesting findings we got,” stated Dr. Marc Friedländer, a scientist with the Wenner-Gren Institute at Stockholm University.
“The muscle-specific microRNAs we discovered in massive tissues are direct proof of gene policy occurring in genuine time in ancient times. It is the very first time something like this has actually been attained.”
The microRNAs that were determined likewise assisted the authors validate that the findings actually originated from mammoths.
“We discovered uncommon anomalies in particular microRNAs that supplied a smoking-gun presentation of their massive origin,” stated Dr. Bastian Fromm, a scientist at the Arctic University Museum of Norway.
“We even spotted unique genes entirely based upon RNA proof, something never ever before tried in such ancient remains.”
“RNA particles can endure a lot longer than formerly believed.”
“Our outcomes show that RNA particles can endure a lot longer than formerly believed,” Professor Dalén stated.
“This implies that we will not just have the ability to study which genes are ‘switched on’ in various extinct animals, however it will likewise be possible to series RNA infections, such as influenza and coronaviruses, maintained in Ice Age stays.”
The outcomes were released on November 14, 2025 in the journal Cell
_____
Emilio Mármol-Sánchez et alAncient RNA expression profiles from the extinct woolly massive. Cellreleased online November 14, 2025; doi: 10.1016/ j.cell.2025.10.025
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.







