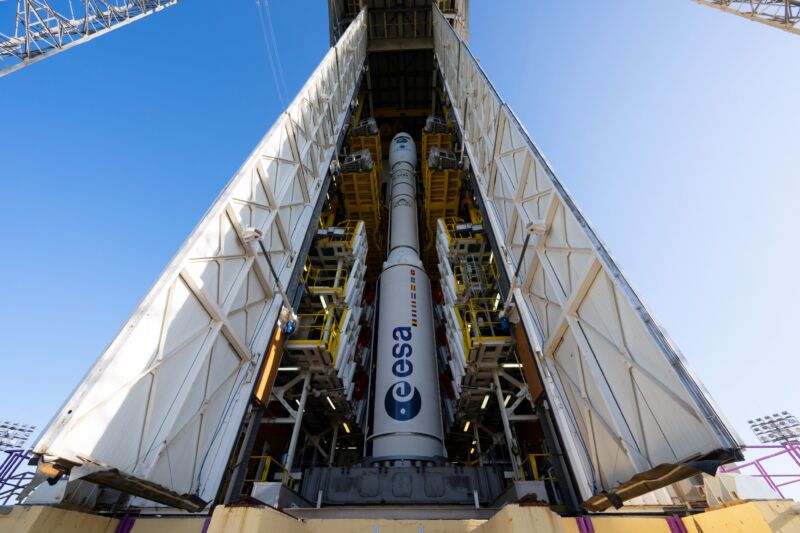
Increase the size of / The last Vega rocket on its launch pad in Kourou, French Guiana.
The last flight of Europe’s Vega rocket is set up for liftoff Wednesday night from French Guiana, bring a crucial ecological tracking satellite for the European Union’s flagship Copernicus program.
The launch is set for 9:50 pm EDT Wednesday (01:50 UTC Thursday) from the European-run spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana. The 98-foot-tall (30-meter) Vega rocket will head north from the launch pad on the coast of South America, going for a polar orbit about 480 miles (775 kilometers) above the Earth.
The sole payload is Sentinel-2C, a remote picking up platform set to sign up with Europe’s fleet of Copernicus ecological satellites. The multibillion-dollar Copernicus system is the world’s most thorough space-based Earth observation network, with satellites fitted with various sort of instruments keeping an eye on land surface areas, oceans, and the environment.
Sentinel-2C will change Sentinel-2A, which introduced on a Vega rocket in 2015 and is nearing completion of its life. A similar satellite called Sentinel-2B has actually remained in orbit because 2017 and will be changed by Sentinel-2D in 2028.
The spacecraft in Europe’s Sentinel-2 series resemble the United States federal government’s Landsat satellites, offering wide-angle optical views of crops, forests, and city locations to track modifications season to season and year to year. The European Commission– the European Union’s executive arm– shares all the Copernicus information complimentary of charge to users worldwide.
The Vega launcher is powered by 3 solid-fueled rocket motors, shooting one after the other, and a liquid-fueled upper phase called the AVUM (the Attitude Vernier Upper Module) that sparks its engine numerous times to position satellites into a little various orbits. Vega can provide up to 3,300 pounds (1,500 kgs) of payload mass into a 435-mile-high (700-kilometer) orbit.
Avio, an Italian aerospace business, developed Vega and supervises a commercial consortium that produces strong motors, structures, and avionics for the rocket. From the start, Arianespace, the French launch company, has actually been accountable for marketing and sales for the Vega program.
The Vega rocket will be changed by the bigger Vega-C rocket, with a more effective booster phase and a larger payload fairing. Among the main functions of the Vega-C will be to introduce future Copernicus satellites for Europe.
“I believe it was a fantastic success,” stated Giulio Ranzo, Avio’s CEO, in an interview with Ars. “It was our very first launcher. It was our very first experience as a significant gamer in the launcher domain. We put it together from a tidy sheet of paper, so the tradition is extremely, really strong. We have actually found out a lot.”
22 and done
In a lots years of service, the Vega rocket never ever actually took off in the business launch market. It balanced about 2 flights annually and mostly released satellites for the European Space Agency and other European federal government firms, which choose releasing their payloads on European rockets.
In the very first couple of years after its launching launch in 2012, it appeared that the Vega rocket may be competitive for agreements to introduce little Earth observation satellites for industrial business and federal government consumers beyond Europe.
A Vega rocket introduced an Earth-imaging satellite for Kazakhstan in 2013, and subsequent objectives provided comparable satellites to orbit for the federal governments of Peru, Turkey, and Morocco. For those objectives, the federal governments tapped European producers Airbus Defense and Space and Thales Alenia Space to develop the satellites and handle their launch agreements. Jet and Thales selected Arianespace, another European business, to introduce these satellites on Vega rockets.
In 2019, a Vega rocket stopped working throughout launch with a military reconnaissance satellite for the United Arab Emirates, ending a streak of 14 straight effective flights, an impressive record for a brand name brand-new launcher.
A year later on, another Vega rocket disappointed orbit and ruined 2 Spanish and French satellites. Simply 2 years after the Vega rocket began flying, the European Space Agency (ESA) authorized the advancement of its replacement, the Vega-C, to manage much heavier payloads.
“We’ve found out a lot,” Ranzo stated. “We have actually had the ability to ideal particular subsystems in Vega that are considerably enhanced in Vega-C. It was what it was implied to be. It was to be our very first experience, and in 12 years, we’ve discovered a lot and put all we have actually found out into a brand-new variation of the rocket.”
The Vega-C released effectively for the very first time in July 2022 however stopped working on its 2nd flight 5 months later on. It hasn’t flown ever since, and engineers have actually upgraded the nozzle for the Vega-C’s 2nd phase strong rocket motor to repair the issue that resulted in the failure in December 2022.
The Vega rocket’s battles with dependability accompanied growing competitors in the industrial launch market. Vega, based upon an expendable style, was overpriced to be competitive with SpaceX, which began using rideshare flights on its workhorse Falcon 9 rocket in 2021.
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.