data-new-v2-image=”true”src=”https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/je9kA8ERVrAHTiVbB65Mnb.jpg” data-pin-media=”https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/je9kA8ERVrAHTiVbB65Mnb.jpg” data-pin-nopin=”true” fetchpriority=”high”>
Over the previous 2 centuries, vaccines have actually been vital for avoiding transmittable illness. The World Health Organization approximates that vaccination avoids in between 3 million and 5 million deaths each year from illness like diphtheria, tetanus influenzameasles and, more just recently, COVID-19
While there has actually long been broad clinical agreement that vaccines avoid or reduce the spread of infections, there is brand-new research study recommending that the healing
effect may surpass the advantage of avoiding contagious illness.
An April 2025 research study released in the popular journal Nature discovered alluring proof that the herpes zoster– or shingles– vaccine might decrease the threat of dementia in the basic population by as much as 20 %.We are a group of doctor researchers with knowledge in the medical and fundamental science of neurodegenerative conditions and dementia
Our company believe that this research study possibly unlocks to other advancements in understanding and dealing with dementia and other degenerative conditions of the brain
A function for vaccines in minimizing dementia danger?Among the significant difficulties scientists deal with when attempting to study the results of vaccines is discovering an unvaccinated “control group” for contrast– a group that resembles the vaccine group in all aspects, conserve for the truth that they have not gotten the active vaccine. That’s due to the fact that it’s dishonest to appoint some clients to the control group and deny them of vaccine security versus an illness such as shingles.
The Nature research study benefited from a policy modification in Wales that entered into impact in 2013, specifying that individuals born upon or after September 2, 1933, were qualified for the herpes zoster vaccination for a minimum of a year, while those born before that cutoff date were not. The vaccine was administered to avoid shinglesan agonizing condition brought on by the very same infection that triggers chickenpox, which can lie inactive in the body and be reactivated later on in life.
Get the world’s most remarkable discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
Related: Shingles vaccine might straight defend against dementia, research study tips
The scientists utilized the policy modification as a natural lab of sorts to study the impact of shingles vaccination on long-lasting health results. In a statistically advanced analysis of health records, the group discovered that the vaccine lowered the likelihood of getting dementia by one-fifth over a seven-year duration. This suggests that individuals who got the shingles vaccine were less most likely to establish medical dementia over the seven-year follow-up duration, and ladies benefited more than males.
The research study style enabled scientists to compare 2 groups without actively denying any one group of access to vaccination. The 2 groups were likewise of equivalent age and had comparable medical comorbidities– implying comparable rates of other medical conditions such as diabetes or hypertension.
Arise from this and other associated research studies raise the possibility that vaccines might have a wider function in speculative rehabs outside the world of contagious illness.
These research studies likewise raise intriguing concerns about how vaccines work and how our body immune system can possibly avoid dementia.
How vaccines may be protectiveOne clinical description for the decrease of dementia by the herpes zoster vaccine might be the direct defense versus the shingles infection, which might contribute in worsening dementia
There is likewise the possibility that the vaccine might have provided security by triggering the immune system and supplying “trained immunity,” in which the body immune system is reinforced by duplicated direct exposure to vaccines or infections.
The research study did not separate in between various kinds of dementia, such as dementia due to Alzheimer’s illness or dementia due to stroke. In addition, scientists can not draw any conclusive conclusions about possible systems for how the vaccines might be protective from an analysis of health records alone.
The next action would be a potential, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled research study– the “gold standard” for scientific trials in medication– to straight analyze how the herpes zoster vaccine compares to a placebo in their capability to minimize the danger of dementia with time. Such research studies are essential before any vaccines, along with other possible treatments, can be suggested for regular scientific usage in the avoidance of dementia.
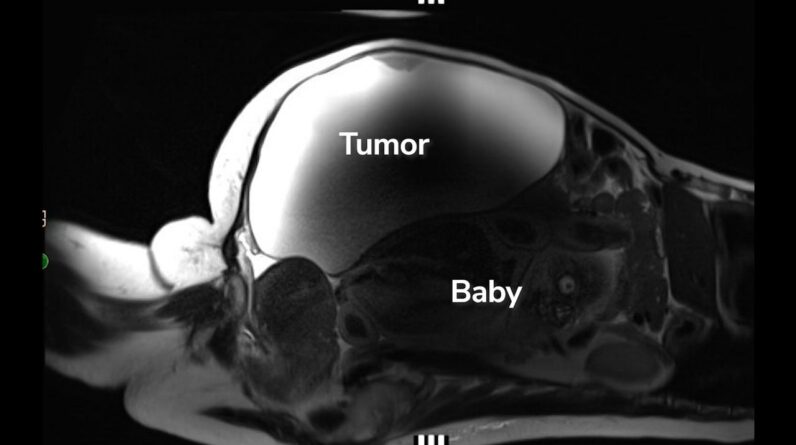
Randomized, placebo-controlled trials are required in order to figure out how the shingles vaccine compares to a placebo with time in securing versus dementia. (Image credit: Radiological Society of North America)The difficulties of untangling dementiaDementia is a significant noncommunicable illness that is a leading cause of death worldwide
A January 2025 research study offered upgraded figures on life time dementia danger throughout various subsets of the U.S. population. The scientists approximate that the life time threat of dementia after age 55 is 42%– more than double earlier quotes. The dementia danger was 4% by age 75, and 20% by age 85, with most of danger taking place after 85. The scientists predicted that the variety of brand-new cases of dementia in the U.S. would fold the next 4 years from around 514,000 cases in 2020 to 1 million in 2060.
As soon as thought about an illness mainly restricted to the industrialized world, the negative results of dementia are now obvious throughout the world, as life span increases in numerous previously establishing nations. While there are various types of dementia with differing medical symptoms and underlying neurobiology, Alzheimer’s illness is the most typical
Potential research studies that particularly evaluate how providing a vaccine alters the threat for future dementia might gain from studying client populations with particular kinds of dementia due to the fact that each variation of dementia may need unique treatments.
For the previous 2 to 3 years, the amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s illness — which presumes that build-up of a protein called amyloid in the brain adds to the condition– controlled the clinical discussionAs an outcome, the majority of the efforts in the speculative rehabs of Alzheimer’s illness have actually concentrated on drugs that lower the levels of amyloid in the brain.
Results to date have actually been modest and frustratingThe 2 just recently authorized amyloid-lowering treatments have just a very little influence on slowing the decreaseare costly and have possibly major adverse effects. And no drug presently authorized by the Food and Drug Administration for medical usage reverses the cognitive decrease.
Research studies based upon health records recommend that previous direct exposure to infections increase the danger of dementiawhile regular vaccines, consisting of those versus tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis, pneumonia, shingles and others, decrease the danger
Development and an open mindThere is often a propensity amongst researchers to hold on to older, familiar designs of illness and a hesitation to relocate more non-traditional instructions.The procedure of doing science has a method of mentor scientists like us humbleness, opening our minds to brand-new details, discovering from our errors and going where that information takes us in our mission for reliable, lifesaving treatments.
Vaccines might be among those courses less took a trip. It is an amazing possibility that might unlock to other developments in understanding and dealing with degenerative conditions of the brain.
This edited post is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Check out the initial short article
Dr. Anand Kumar is the head of psychiatry at the University of Illinois at Chicago. His research study concentrates on late-life anxiety and mental illness of the senior, consisting of Alzheimer’s illness, and he has actually been constantly moneyed by the NIH for over 18 years. Commonly acknowledged as a leader in geriatric psychiatry, he has actually released more than 100 peer-reviewed documents and got the Jack Weinberg Award for Geriatric Psychiatry from the American Psychiatric Association.
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.