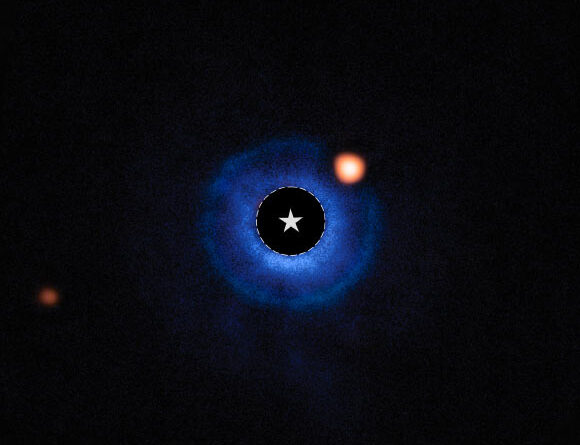
Astronomers have actually utilized the extraordinary level of sensitivity of the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) onboard the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope in the thermal infrared to look for exoplanets in the three-ring particles disk around the 6.4-million-year-old star TWA 7.
[
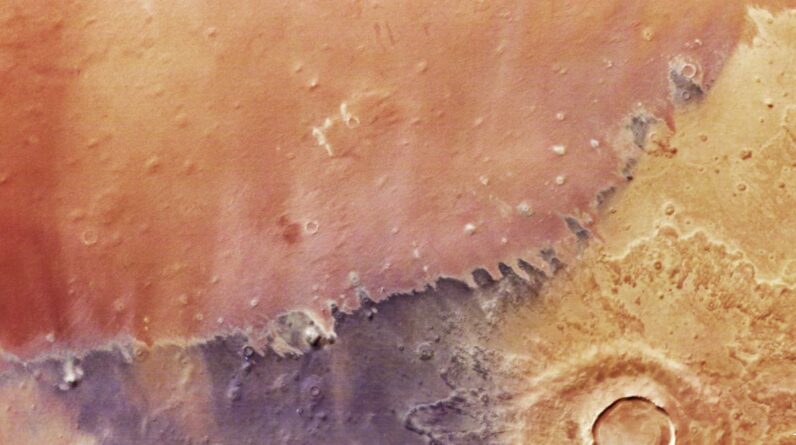
This Webb/MIRI image reveals the Saturn-mass exoplanet TWA 7b. Image credit: NASA/ ESA/ CSA/ Webb/ A.M. Lagrange/ M. Zamani, ESA & Webb.
Particles disks filled with dust and rocky product are discovered around both young and older stars, although they are more quickly identified around more youthful stars as they are brighter.
They typically include noticeable rings or spaces, believed to be produced by worlds that have actually formed around the star.
TWA 7 is a young, low-mass (0.46 solar masses) M-type star situated about 111 light-years away in the constellation of Antlia.
Understood as CE Antilae or TYC 7190-2111-1, the star is a member of the TW Hydra association.
Its almost face-on three-ring particles disk made it a perfect target for Webb’s high-sensitivity mid-infrared observations.
“Our observations expose a strong prospect for a world forming the structure of the TWA 7 particles disk, and its position is precisely where we anticipated to discover a world of this mass,” stated Dr. Anne-Marie Lagrange, an astronomer at the Observatoire de Paris-PSL, the Université Grenoble Alpes and CNRS.
Utilizing the coronagraph on Webb’s MIRI instrument on June 21, 2024, Dr. Lagrange and coworkers thoroughly reduced the intense glare of the host star to expose faint neighboring things.
This method, called high-contrast imaging, makes it possible for astronomers to straight spot worlds that would otherwise be lost in the frustrating light from their host star.
After deducting recurring starlight utilizing innovative image processing, a faint infrared source was exposed near TWA 7, appreciable from background galaxies or planetary system things.
The source lies in a space in among 3 dust rings that were found around TWA 7 by previous ground-based observations.
Its brightness, color, range from the star, and position within the ring follow theoretical forecasts for a young, cold, Saturn-mass world shaping the surrounding particles disk.
“This observatory allows us to record pictures of worlds with masses comparable to those in the planetary system, which represents an interesting advance in our understanding of planetary systems, including our own,” stated Dr. Mathilde Malin, an astronomer at Johns Hopkins University and the Space Telescope Science Institute.
The group’s preliminary analysis recommends that the item, called TWA 7b, might be a young, cold exoplanet with a mass around 0.3 times that of Jupiter (100 Earth masses) and a temperature level near 320 K (approximately 47 degrees Celsius).
Its area (about 52 AU from the star) lines up with a space in the disk, meaning a vibrant interaction in between the world and its environments.
As soon as confirmed, this discovery would mark the very first time a world has actually been straight related to shaping a particles disk and might use the very first observational tip of a Trojan disk– a collection of dust caught in the world’s orbit.
“The findings highlight Webb’s capability to check out formerly hidden, low-mass worlds around close-by stars,” the astronomers stated.
“Ongoing and future observations will intend to much better constrain the residential or commercial properties of the prospect, validate its planetary status, and deepen our understanding of world development and disk development in young systems.”
“This initial outcome showcases the amazing brand-new frontier that Webb is opening for exoplanet discovery and characterization.”
The discovery is explained in a paper in the journal Nature
_____
A-M. Lagrange et alProof for a sub-Jovian world in the young TWA 7 disk. Naturereleased online June 25, 2025; doi: 10.1038/ s41586-025-09150-4
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.