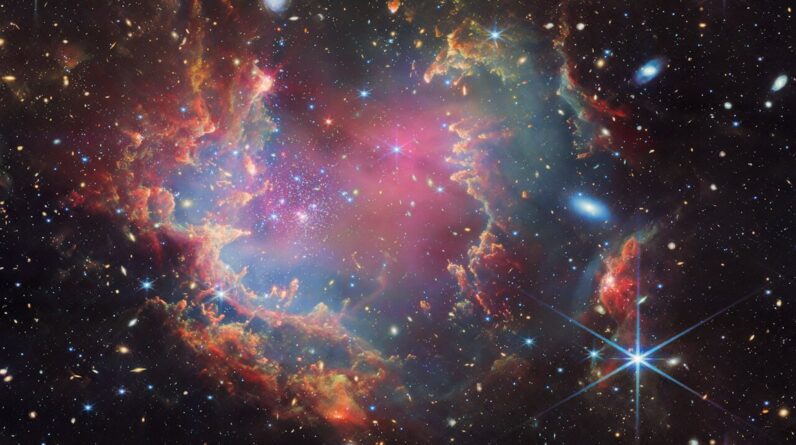
The James Webb Space Telescope’s view of the star cluster NGC 602 in the neighboring Small Magellanic Cloud exposes intense young stars(blue)and clouds of dust shaped by excellent radiation.
(Image credit: ESA/Webb, NASA & CSA, P. Zeidler, E. Sabbi, A. Nota, M. Zamani (ESA/Webb))
Astronomers utilizing the James Webb Space Telescope ( JWST )have actually glanced over the Milky Way’s back fence and discovered that there’s something unusual about the outstanding babies playing next door.
While focusing on the young star cluster NGC 602 in the neighboring Small Magellanic Cloud(SMC), the scientists identified what might be the very first proof of brown overshadows ever seen outside the Milky Way. Brown overshadows, or “failed stars,” are strange things that are larger than the biggest worlds however not enormous sufficient to sustain nuclear blend like stars.
The observations, that include a spectacular brand-new picture of the star cluster thanks to JWST’s Near Infrared Camera, expose fresh insight into how these odd stopped working stars form. The group released its research study Oct. 23 in The Astrophysical Journal
“Brown dwarfs seem to form in the same way as stars, they just don’t capture enough mass to become a fully fledged star,” lead research study author Peter Zeidlera scientist at the European Space Agency (ESA), stated in a declaration “Our results fit well with this theory.”
NGC 602 is an approximately 3 million-year-old star-forming cluster on the borders of the SMC, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way which contains approximately 3 billion stars(Our galaxy, in contrast, consists of an approximated 100 billion to 400 billion stars.) Orbiting about 200,000 light-years from Earth, the SMC is among the Milky Way’s closest intergalactic next-door neighbors and a regular target for huge research studies.
Related: Runaway ‘stopped working star’ races through the universes at 1.2 million miles per hour
Previous observations of NGC 602 taken with the Hubble Space Telescope exposed that the cluster hosts a population of young, low-mass stars. Now, thanks to JWST’s unbelievable level of sensitivity to infrared light, astronomers have actually expanded the image of these excellent babies, exposing exactly just how much mass they have actually built up in their brief lives.
Get the world’s most interesting discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
The outcomes recommend that 64 excellent items within the cluster have masses varying in between 50 and 84 times that of JupiterBrown overshadows generally weigh in between 13 and 75 Jupiter masses, according to ESA– making a lot of these items prime prospects to be the very first brown overshadows spotted beyond our galaxy.
These stopped working stars appear to have actually formed in similar method as stars like the sun: through the collapse of huge clouds of gas and dust. For a collapsed cloud to end up being a star, it needs to continue collecting mass up until it reaches an internal temperature level and pressure high sufficient to activate hydrogen combination at its core– integrating hydrogen atoms into helium and launching energy as light and heat in the procedure.
Brown overshadows never ever get adequate mass to sustain long-term blend, leaving them bigger than a world however smaller sized and dimmer than a star. This failure to spark might be a typical result in deep space: Astronomers have actually found about 3,000 brown overshadows in the Milky Way however approximate that there might be as lots of as 100 billion in our galaxy alone, possibly making them as typical as stars themselves.
Studying this group of extragalactic stopped working stars even more might assist clarify why many stars relatively stop working to spark. According to the scientists, these oddball items might likewise expose brand-new insights about the early universe. NGC 602 is a young cluster including low abundances of components much heavier than hydrogen and helium, so its structure is believed to be really comparable to that of the ancient universe, previously later on generations of stars peppered the universes with the panoply of components we see near Earth.
“By studying the young metal-poor brown dwarfs newly discovered in NGC 602, we are getting closer to unlocking the secrets of how stars and planets formed in the harsh conditions of the early Universe,” research study co-author Elena Sabbia researcher at the National Science Foundation’s NOIRLab, the University of Arizona and the Space Telescope Science Institute, stated in a 2nd declaration
Brandon is the space/physics editor at Live Science. His writing has actually appeared in The Washington Post, Reader’s Digest, CBS.com, the Richard Dawkins Foundation site and other outlets. He holds a bachelor’s degree in innovative composing from the University of Arizona, with minors in journalism and media arts. He takes pleasure in composing most about area, geoscience and the secrets of deep space.
A lot of Popular
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.