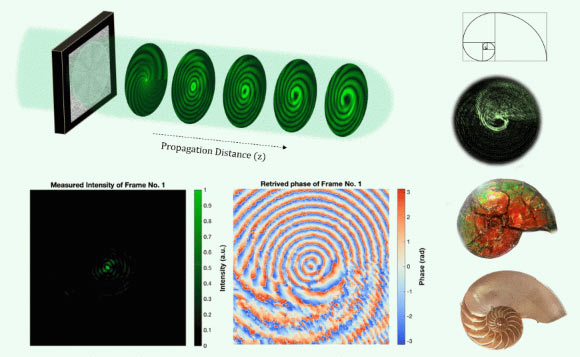
The structure of optical rotatum follows a logarithmic spiral– a signature that is typically seen in the pattern development of seashells and galaxies, according to a group of physicists from Harvard University.
Advancement of a beam bring optical rotatum as a function of proliferation range. Image credit: Dorrah et aldoi: 10.1126/ sciadv.adr9092.
“This is a brand-new habits of light including an optical vortex that propagates through area and modifications in uncommon methods, “stated Professor Federico Capasso, senior authors of the research study.
“It is possibly helpful for controling little matter.”
In a strange twist, the scientists discovered that the orbital angular momentum-carrying beam grows in a mathematically identifiable pattern discovered all over the natural world.
Mirroring the Fibonacci number series, their optical rotatum propagates in a logarithmic spiral that is seen in the shell of a nautilus, the seeds of a sunflower, and the branches of trees.
“That was among the unanticipated highlights of this research study,” stated Dr. Ahmed Dorrah, very first author of the research study.
“Hopefully we can motivate others who are professionals in used mathematics to more research study these light patterns and acquire distinct insights into their universal signature.”
This research study constructs on previous operate in which the group utilized a metasurface, a thin lens engraved with light-bending nanostructures, to produce a beam with regulated polarization and orbital angular momentum along its proliferation course, transforming any input of light into other structures that alter as they move.
Now, they’ve presented another degree of flexibility to their light, in which they can likewise alter its spatial torque as it propagates.
“We reveal much more adaptability of control, and we can do it continually,” stated Alfonso Palmieri, a co-author of the research study.
Possible usage cases for such an unique beam consist of the control of really little particles, such as colloids in suspension, by presenting a brand-new kind of force in accordance with the light’s uncommon torque.
It might likewise allow an exact optical tweezer for micro-manipulation of little things.
While others have actually shown torque-changing light utilizing high-intensity lasers and large setups, the researchers made theirs with a single liquid crystal screen and a low-intensity beam.
By revealing they can produce a rotatum in an industry-compatible, integrated gadget, the barrier to entry for their innovation to end up being truth is much lower than previous presentations.
“Our work broadens the previous literature on structured light, provides brand-new techniques for light-matter interaction, interactions, and picking up, and mean comparable results in condensed matter physics and Bose-Einstein condensates,” they concluded.
The research study was released in the journal Science Advances
_____
Ahmed H. Dorrah et al2025. Rotatum of light. Science Advances 11 (15 ); doi: 10.1126/ sciadv.adr9092
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.







