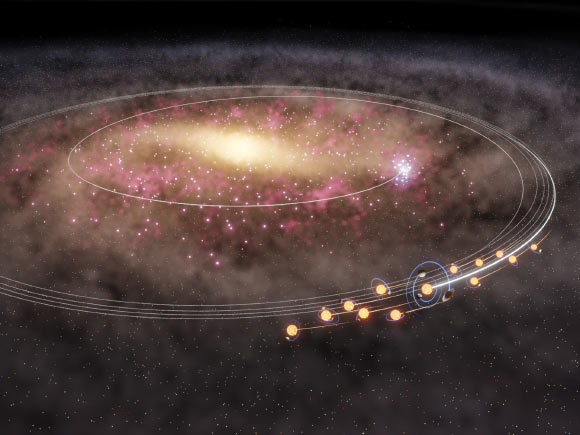
After 1I/ ʻOumuamua and 2I/Borisov, 3I/ATLAS is the 3rd item and the 2nd comet from outside the Solar System verified.
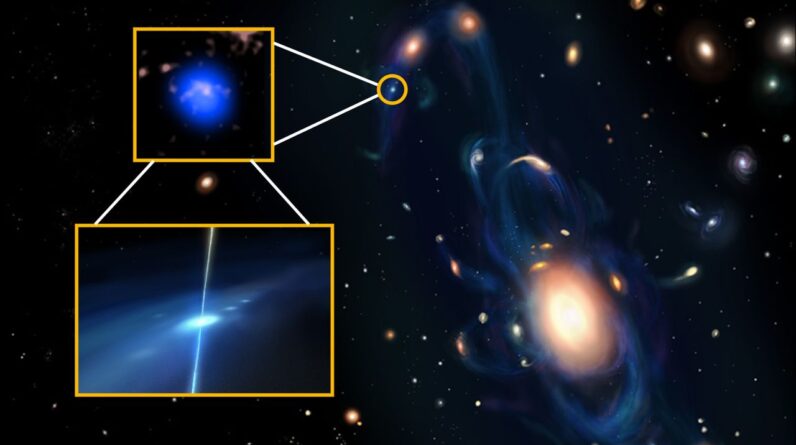
This image from the Multi-Object Spectrograph(GMOS-N)at the Gemini North telescope reveals the interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS. Image credit: International Gemini Observatory/ NOIRLab/ NSF/ AURA/ & K. Meech, IfA & U. Hawaii/ Jen Miller & Mahdi Zamani, NOIRLab.
3I/ATLAS was found by the NASA-funded Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) on July 1, 2025.
Understood as C/2025 N1 (ATLAS) and A11pl3Z, the comet showed up from the instructions of the constellation Sagittarius.
Its orbit is the most dynamically severe of any things yet tape-recorded in the Solar System.
“It may not be aliens making very first contact, yet 3I/ATLAS, as just the 3rd recorded interstellar challenge travel through the Solar System, still has plenty to teach us,” stated Northeastern University astronomer Jacqueline McCleary.
“Interstellar things, which all appear to be comets, are the only things that we’ve ever gotten physical observations for within our Solar System that came from outside the Solar System. This is sort of like a messenger afar.”
“There are so couple of interstellar items that we’ve spotted in our Solar System, and they each appear to be special,” stated Michigan State University astronomer Adina Feinstein.
“3I/ATLAS provides us a chance to study other planetary systems up close and individual, without really requiring to visit them.”
The minute astronomers found 3I/ATLAS, it was clear it was not a regular comet. For beginners, it appeared to be discharging its own light, which is strange for a comet that was, at that time, up until now from the Sun.
Comets are generally exceptionally dark to the point where astronomers have a hard time to see them.
As they get closer to the Sun, solar radiation triggers unstable substances and ices on their outdoors, which are extremely reflective, to melt.
The resulting result is, in the beginning, a sort of proto-tail called a coma, which turns into the tail we have actually concerned connect with comets spotting through the night sky.
“Jupiter is 5 AU or 5 Earth-Sun ranges far from the Sun, and many comets need to get closer than that for the solar radiation to get extreme adequate to begin this melting, outgassing tail production,” Dr. McCleary stated.
“Comet 3I/ATLAS formed a coma when it was outside the orbit of Jupiter, at a much higher range than was regular.”
For 3I/ATLAS to have actually begun radiant as far out from the Sun as it did was unusual adequate to lead to some thinking early on that it needs to be an alien spacecraft. What else that little and fast would be producing light?
Subsequent observations exposed it not just had a comet-like tail however that it was most likely abundant in carbon dioxide”due to the fact that carbon dioxide ice, aka dry ice, melts extremely quickly
The NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope eventually exposed the comet was special for factors that surpassed its interstellar origins.
Not just was it made from co2, however it had a co2 ice-to-water ice ratio that was actually out of this world, 8:1, which is amongst the greatest ever tape-recorded.
It uses a prospective look into the conditions that exist in other planetary systems and how those systems formed in the very first location.
“Clearly, the 3I/ATLAS moms and dad system possibly was actually abundant in co2 or perhaps there were strange radiation procedures that left a great deal of co2 and boiled away whatever else,” Dr. McCleary stated.
“Indirectly, attempting to comprehend the structure of this comet and comparing it to the structure of other interstellar comets … can inform us about what planetary system development appears like in other planetary systems at an actually granular level.”
It’s still uncertain where specifically 3I/ATLAS stemmed from.
“It likely originated from the Milky Way bulge, however tracing its specific origin will be hard,” Dr. McCleary stated.
“In order for it to have actually left its moms and dad planetary system, the comet should have come across a gravitational perturbation that interrupted its orbital course and set it on course to enter our Solar System.”
Researchers might get an even more in-depth peek of the comet when it crosses the orbit of Jupiter on its outward-bound course after October, exposing more about its nature.
NASA’s Jupiter-orbiting Juno satellite will remain in the very best position to put eyes on the interstellar visitor.
“We might possibly get an extremely close take a look at that comet, and it might be especially fascinating due to the fact that it will have gone as near the sun as it’s going to get and great deals of co2 will have boiled off … so we’ll have the ability to see what’s left,” Dr. McCleary stated.
Discovering more about 3I/Atlas will not just work for comprehending what other planetary systems resemble, however why our Solar System is so distinct that it produced the conditions for sentient life to exist.
“It’s a window into what the beautiful product is for other planetary systems, which is valuable, and, in turn, assists us improve our designs of what planetary system development can appear like,” Dr. McCleary stated.
“Is our Solar System typical or unusual? It appears to be fairly unusual, and this assists us measure that.”
“Learning about other planetary systems locations humankind into context,” Dr. Feinstein stated.
“One of life’s biggest concerns is ‘are we alone in deep space?’ Each NASA objective gets us a bit more detailed to addressing this huge, overarching concern.”
“Capturing as numerous observations from the prediscovery duration, where 3I/ATLAS might remain in telescope images however wasn’t formerly recognized, is vital to our understanding of how these items ‘switch on’ as they approach our Sun,” stated Auburn University astronomer John Noonan.
“These interstellar items have actually most likely not been warmed substantially in millions, if not billions, of years, and any chance to see how they reacted to that early heating is of interest.”
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.