We’re going to require more X’s
“This marks not simply the next chapter, however the next book in SpaceX and xAI’s objective.”
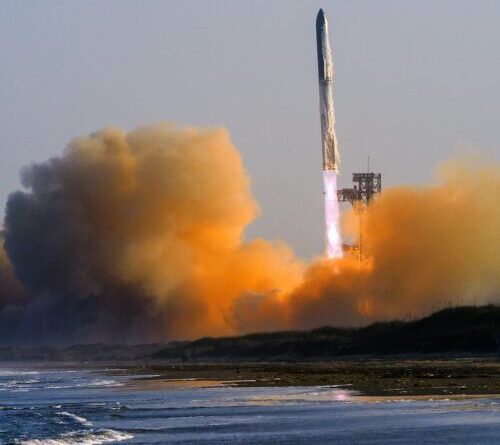
SpaceX’s Starship and Super Heavy booster take off from Starbase, Texas, in March 2025.
Credit: SpaceX
SpaceX has actually officially obtained another among Elon Musk’s business, xAi, the area business revealed on Monday afternoon.
“SpaceX has actually gotten xAI to form the most enthusiastic, vertically-integrated development engine on( and off )Earth, with AI, rockets, space-based web, direct-to-mobile gadget interactions and the world’s primary real-time details and complimentary speech platform, “the business stated.”This marks not simply the next chapter, however the next book in SpaceX and xAI’s objective: scaling to make a sentient sun to comprehend deep space and extend the light of awareness to the stars!”
The combining of what is perhaps Musk’s most effective business, SpaceX, with the more speculative xAI endeavor is a threat. Established in 2023, xAI’s primary items are the generative AI chatbot Grok and the social networks website X, previously called Twitter. The business intends to take on OpenAI and other expert system companies. Grok has actually been questionable, consisting of the sexualization of ladies and kids through AI-generated images, as has Musk’s management of Twitter.
Vertically incorporating AI and area
There can be no concern that the merger of SpaceX– the world’s best spaceflight business– and the expert system company use prospective tactical advances. Musk highly thinks that expert system is main to mankind’s future and wishes to be amongst those leading in its advancement. With this merger, he prepares to utilize SpaceX’s deep proficiency in quick launch and satellite production and management to release a constellation of up to 1 million orbital information. This will supply the foundation of calculating power required to support xAI’s operations.
Musk’s prepare for the merged business is asserted on numerous presumptions, consisting of that AI is not a bubble, however rather an innovation that will be totally accepted in the future; that orbital information centers are cost-competitive compared to ground-based information centers; which calculate is the important obstruction that should be resolved for prevalent adoption of AI by society.
If these presumptions hold true, the merged SpaceX-xAI business holds an effective position. It might possibly own a complete stack of abilities, from launch to orbital bandwidth to frontier AI designs, and with Starlink Internet, it might supply AI as needed, throughout the world, to any mobile phone.
SpaceX currently has the world’s workhorse recyclable rocket with the Falcon 9. It can currently provide about 20 heaps to low-Earth orbit for an internal expense of $15 million, compared to more than 4 or 5 times that on the free market. SpaceX is working towards a completely multiple-use incredibly heavy lift rocket with its Starship lorry.
The independently held business likewise runs more satellites, about 9,600, than any other nation or business worldwide by an element of 10. It has substantial operations not simply in releasing however likewise in running this constellation over the last years. This is not a basic ability.
“I would state there have actually been as numerous engineering improvements in orbital security and crash avoidance in the last 10 years as there have actually been advances in rocketry, which might have gone undetected,” stated Brian Weeden, director of civil and industrial policy at The Aerospace Corporation, in an interview.
“Happening actually quick”
In an e-mail to SpaceX workers on Monday, Musk stated Starship will start releasing V3 Starlink satellites into orbit this year, in addition to the next generation of direct-to-mobile satellites. The launches, he stated, will be a “forcing function” to enhance the efficiency of Starship, making it more quickly multiple-use for information center release.
“The large variety of satellites that will be required for space-based information centers will press Starship to even higher heights,” Musk composed. “With launches every hour bring 200 lots per flight, Starship will provide countless lots to orbit and beyond annually, making it possible for an amazing future where humankind is out checking out among the stars.”
Musk informed staff members that introducing 1 million heaps each year of satellites, creating 100 kW of calculate power per heap, would include 100 gigawatts of AI calculate capability yearly, “without any continuous functional or upkeep requirements.” Eventually, Musk thinks there is a course to introducing 1 TW/year from Earth.
“My quote is that within 2 to 3 years, the most affordable expense method to create AI calculate will remain in area,” Musk composed. “This cost-efficiency alone will make it possible for ingenious business to advance in training their AI designs and processing information at unmatched speeds and scales, speeding up advancements in our understanding of physics and innovation of innovations to benefit mankind.”
Musk is plainly bullish on the future of AI and on area’s capacity to attend to the ravenous power requirements of AI information. Many individuals in the AI market hypothesize that expert system is most likely to go through major and continual growing discomforts, or doubt that space-based information centers can take on operations constructed on the ground. Musk, more than anybody, has the ways to push forward the bull case for space-based AI, and he is going for it.
Monday’s merger follows an ultra-ambitious filing on Friday with the Federal Communications Commission in which SpaceX looked for authorization to release 1 million satellites that will run as “orbital information centers.” The business stated it would release the satellites to orbits with an elevation in between 500 and 2,000 km, and 30-degree and Sun-synchronous dispositions.
SpaceX likewise just recently revealed its strategies to release an area situational awareness system, called Stargaze, that will utilize star trackers to offer information on possible combinations in between satellites in orbit. The objective is to assist de-conflict satellite trajectories and prevent crashes in low-Earth orbit.
“This is all taking place truly quickly,” stated Victoria Samson, primary director of area security and stability for Secure World Foundation, in an interview.
Crowded orbits
Samson stated that, at present, satellites have a relatively big “bubble” of area around them when it concerns crash detection. This is since of unpredictabilities in the exact area and motion of automobiles. If you enhance area situational awareness, such as what SpaceX looks for to do with Stargaze, those bubbles might be diminished to lower the variety of prospective crash cautions. That will come with dangers.
“There’s a great deal of space in area, obviously,” Samson stated. “But the concern is, just how much threat do you wish to take?”
A technical professional at The Aerospace Corporation, Marlon Sorge, informed Ars that numerous unanswered concerns about SpaceX’s proposed megaconstellation for orbital information centers make it hard to examine the threats of accident. This includes their size (they will need large solar ranges to gather sunshine) and exactly where the satellites will be released. There is currently a great deal of particles at around 800 to 1,000 km above Earth from previous crashes, consisting of from a notorious Chinese anti-satellite rocket test in 2007, which produced more than 3,000 pieces of golf-ball-size or bigger particles.
Above that elevation, there is less particles, Sorge stated. Things at that elevation take centuries to deorbit naturally, due to the extremely minimal environment.
“The huge difficulty at those elevations is the things that’s up there keeps up there,” Sorge stated. “If you create more particles, if you have issues, it will not disappear, so you’re persevered.”
SpaceX looked for to deal with these issues in its regulative filing, keeping in mind that each satellite would have “redundant maneuverability abilities” in order to deorbit into Earth’s environment. The filing likewise appears to acknowledge emerging science that suggests that aluminum burning up from reentering satellites is damaging to ozone levels. To resolve this, SpaceX is thinking about moving aging satellites into “high elevation Earth orbits or heliocentric orbits.”
Sorge kept in mind that the quantity of energy, or delta-V, required to move a satellite from low-Earth orbit into a heliocentric orbit is “non-trivial.”
Has SpaceX lost its method?
Among the lots of concerns raised by the brand-new merger is whether SpaceX has actually lost its method. Musk established the business in 2002 with the particular function of settling Mars, an adventurous if not difficult objective at the time. In the years considering that, SpaceX has actually made reputable development towards Mars, and with Starship, humankind has for the very first time a transport system possibly efficient in landing people on the red world.
Obtaining an AI business and putting so much effort into orbital information? Is this constant with the Mars objective? Musk plainly believes it is.
“While releasing AI satellites from Earth is the instant focus, Starship’s abilities will likewise make it possible for operations on other worlds,” he composed. “Thanks to developments like in-space propellant transfer, Starship will can landing enormous quantities of freight on the Moon. When there, it will be possible to develop an irreversible existence for clinical and production pursuits. Factories on the Moon can make the most of lunar resources to make satellites and release them even more into area.”
And from there, he stated, Mars will be securely on the horizon.
“The abilities we open by making space-based information focuses a truth will money and allow self-growing bases on the Moon, a whole civilization on Mars and eventually growth to deep space,” he composed.
That’s the vision, a minimum of.
Eric Berger is the senior area editor at Ars Technica, covering whatever from astronomy to personal area to NASA policy, and author of 2 books: Liftoffabout the increase of SpaceX; and Reentryon the advancement of the Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon. A licensed meteorologist, Eric resides in Houston.
551 Comments
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.