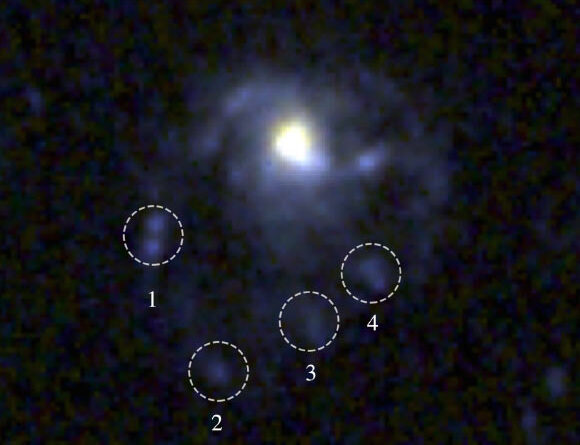
Scientist discovered Antarctica’s very first piece of amber in sediment cores gathered from the seafloor off the icy continent’s coast.
(Image credit: Alfred-Wegener-Institut/ V. Schumacher)
For the very first time, scientists have actually found a piece of fossilized resin, or amber, in Antarctica. The small golden piece, uncovered underneath the seafloor, consists of tiny residues of an ancient dinosaur-era rain forest that stretched throughout the continent 90 million years back, a brand-new research study exposes.
Amber is fossilized resin, or tree sap, that can trap plants, pests, little animals or other raw material with it as it solidifies. The golden-yellow housing is airtight and primarily transparent, implying it both completely protects and shows whatever is inside it, like a transparent time pill.
Previously, amber fossils had actually been discovered on each of Earth’s continents, other than for Antarctica. In the brand-new research study, released Tuesday( Nov. 12 )in the journal Antarctic Sciencescientists recognized a small piece of amber, around 0.002 inch (70 micrometers) throughout, in sediment cores gathered underneath the seafloor at a depth of around 3,100 feet (950 meters)off the coast of Pine Island Glacier on Antarctica’s west coast.
The small piece go back to around 90 million years back throughout the Cretaceous duration (145 million to 66 million years ago ). At this time, big parts of Antarctica were covered by a temperate jungle, comparable to those discovered in New Zealand today, that grew in warmer weather conditions– and a small part of that lost environment is caught within the amber.
“This discovery allows a journey to the past in yet another more direct way,” research study lead author Johann Klagesa sedimentologist at the Alfred Wegener Institute in Germany, stated in a declaration “Our goal now is to learn more about the forest ecosystem.”
Related: Wildfires burned Antarctica 75 million years back, charcoal residues expose
Throughout the Cretaceous duration, big parts of Antarctica were covered by a subtropical rain forest. (Image credit: J. McKay/Alfred-Wegener-Institut)
The sediment cores utilized in the research study were very first gathered in 2017 and were later on exposed to include fossils of roots, pollen, spores and other remains from blooming plantswhich represent a few of the very best proof of Antarctica’s Cretaceous-era rain forest.
Get the world’s most interesting discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
The amber piece was just recently found as scientists separated the staying products into countless small pieces and fastidiously scanned every one utilizing fluorescent microscopy. Additional analysis exposed that it consisted of “micro-inclusions” from bark that would have most likely as soon as lined a conifer-like tree that resided in the ancient forest.
The bark likewise reveals some indications of “pathological resin flow” — a method utilized by trees to seal up damage done to their woody protecting by parasites or wildfires, by producing a chemical and physical barrier with resin.
Microscopic lense pictures of the amber program small pieces of bark entombed in the fossilized resin. (Image credit: Johann P. Klages)
While the brand-new piece is little, it is uncommonly unspoiled in spite of it being buried under the seafloor.
“Considering its solid, transparent and translucent particles, the amber is of high quality,” research study co-author Henny Gerschela specialist at the Saxony State Office for the Environment, Agriculture and Geology in Dresden, Germany, stated in the declaration. The piece should have invested the majority of the last 90 million years near the seafloor’s surface area, “as amber would [normally] dissipate under increasing thermal stress and burial depth,” she included.
The scientists think that their findings might unlock to discovering more Antarctic amber, which might open much more tricks about this ancient jungle and the dinosaurs that resided in it.
“Our discovery is another piece of the puzzle,” Gerschel stated.
Harry is a U.K.-based senior personnel author at Live Science. He studied marine biology at the University of Exeter before training to end up being a reporter. He covers a wide variety of subjects consisting of area expedition, planetary science, area weather condition, environment modification, animal habits, development and paleontology. His function on the upcoming solar optimum was shortlisted in the “top scoop” classification at the National Council for the Training of Journalists (NCTJ) Awards for Excellence in 2023.
The majority of Popular
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.